Your success in Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 is our sole target and we develop all our DOP-C01 braindumps in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our DOP-C01 study material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. DOP-C01 Practice Exams for Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Also have DOP-C01 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
You have a web application that is currently running on a three M3 instances in three AZs. You have an Auto Scaling group configured to scale from three to thirty instances. When reviewing your Cloud Watch metrics, you see that sometimes your Auto Scalinggroup is hosting fifteen instances. The web application is reading and writing to a DynamoDB.configured backend and configured with 800 Write Capacity Units and 800 Read Capacity Units. Your DynamoDB Primary Key is the Company ID. You are hosting 25 TB of data in your web application. You have a single customer that is complaining of long load times when their staff arrives at the office at 9:00 AM and loads the website, which consists of content that is pulled from DynamoDB. You have other customers who routinely use the web application. Choose the answer that will ensure high availability and reduce the customer's access times.
- A. Adda caching layer in front of your web application by choosing ElastiCacheMemcached instances in one of the AZs.
- B. Doublethe number of Read Capacity Units in your DynamoDB instance because theinstance isprobably being throttled when the customer accesses the website andyour web application.
- C. Changeyour Auto Scalinggroup configuration to use Amazon C3 instance types, becausethe web application layer is probably running out of compute capacity.
- D. Implementan Amazon SQS queue between your DynamoDB database layer and the webapplication layer to minimize the large burst in traffic the customergenerateswhen everyone arrives at the office at 9:00AM and begins accessing the website.
- E. Usedata pipelines to migrate your DynamoDB table to a new DynamoDB table with aprimary key that is evenly distributed across your datase
- F. Update your webappl ication to request data from the new table
Answer: E
Explanation:
The AWS documentation provide the following information on the best performance for DynamoDB tables
The optimal usage of a table's provisioned throughput depends on these factors: The primary key selection.
The workload patterns on individual items. The primary key uniquely identifies each item in a table. The primary key can be simple (partition key) or composite (partition key and sort key). When it stores data, DynamoDB divides a table's items into multiple partitions, and distributes the data primarily based upon the partition key value. Consequently, to achieve the full amount of request throughput you have provisioned for a table, keep your workload spread evenly across the partition key values. Distributing requests across partition key values distributes the requests across partitions. For more information on DynamoDB best practises please visit the link:
• http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/Guide I inesForTables.htm I
Note: One of the AWS forumns is explaining the steps for this process in detail. Based on that, while importing data from S3 using datapipeline to a new table in dynamodb we can create a new index. Please find the steps given below.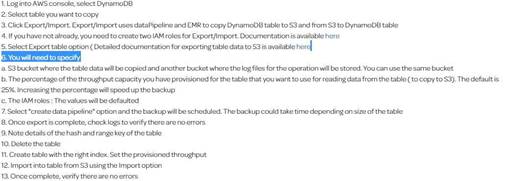
NEW QUESTION 2
Your team is responsible for an AWS Elastic Beanstalk application. The business requires that you move to a continuous deployment model, releasing updates to the application multiple times per day with zero downtime. What should you do to enable this and still be able to roll back almost immediately in an emergency to the previous version?
- A. Enablerolling updates in the Elastic Beanstalk environment, setting an appropriatepause time for application startup.
- B. Createa second Elastic Beanstalk environment running the new application version, andswap theenvironment CNAMEs.
- C. Developthe application to poll for a new application version in your code repository;download and install to each running Elastic Beanstalk instance.
- D. Createa second Elastic Beanstalk environment with the new application version, andconfigure the old environment to redirect clients, using the HTTP 301 responsecode, to the new environment
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the below
Because Elastic Beanstalk performs an in-place update when you update your application versions, your application may become unavailable to users for a short
period of time. It is possible to avoid this downtime by performing a blue/green deployment, where you deploy the new version to a separate environment, and then
swap CNAMCs of the two environments to redirect traffic to the new version instantly For more information on Elastic beanstalk swap URL please see the below link:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/using-features.CNAM CSwap.html
NEW QUESTION 3
A company has developed a Ruby on Rails content management platform. Currently, OpsWorks with several stacks for dev, staging, and production is being used to deploy and manage the application. Now the company wants to start using Python instead of Ruby. How should the company manage the new deployment? Choose the correct answer from the options below
- A. Update the existing stack with Python application code and deploy the application using the deploy life-cycle action to implement the application code.
- B. Create a new stack that contains a new layer with the Python cod
- C. To cut over to the new stack the company should consider using Blue/Green deployment
- D. Create a new stack that contains the Python application code and manage separate deployments of the application via the secondary stack using the deploy lifecycle action to implement the application code.
- E. Create a new stack that contains the Python application code and manages separate deployments of the application via the secondary stack.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Blue/green deployment is a technique for releasing applications by shifting traffic between two identical environments running different versions of the application.
Blue/green deployments can mitigate common risks associated with deploying software, such as downtime and rollback capability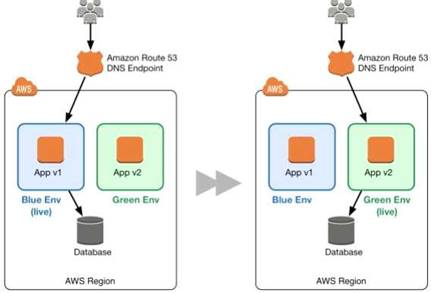
Please find the below link on a white paper for blue green deployments
• https://d03wsstatic.com/whitepapers/AWS_Blue_Green_Deployments.pdf
NEW QUESTION 4
You are using Elastic Beanstalk to manage your application. You have a SQL script that needs to only be executed once per deployment no matter how many EC2 instances you have running. How can you do this?
- A. Use a "Container command" within an Elastic Beanstalk configuration file to execute the script, ensuring that the "leader only" flag is set to false.
- B. Use Elastic Beanstalk version and a configuration file to execute the script, ensuring that the "leader only" flag is set to true.
- C. Use a "Container command" within an Elastic Beanstalk configuration file to execute the script, ensuring that the "leader only" flag is set to true.
- D. Use a "leader command" within an Elastic Beanstalk configuration file to execute the script, ensuring that the "container only" flag is set to true.
Answer: C
Explanation:
You can use the container_commands key to execute commands that affect your application source code. Container commands run after the application and web server have been set up and the application version archive has been extracted, but before the application version is deployed. Non- container commands and other customization operations are performed prior to the application source code being extracted.
You can use leader_only to only run the command on a single instance, or configure a test to only run the command when a test command evaluates to true. Leader-only container commands are only executed during environment creation and deployments, while other commands and server customization operations are performed every time an instance is provisioned or updated. Leader- only container commands are not executed due to launch configuration changes, such as a change in the AMI Id or instance type. For more information on customizing containers, please visit the below URL:
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/customize-containers-ec2.html
NEW QUESTION 5
You are a Devops Engineer for your company. You are planning on using Cloudwatch for monitoring the resources hosted in AWS. Which of the following can you do with Cloudwatch logs ideally. Choose 3 answers from the options given below
- A. StreamthelogdatatoAmazonKinesisforfurtherprocessing
- B. Sendthe log data to AWS Lambda for custom processing
- C. Streamthe log data into Amazon Elasticsearch for any search analysis required.
- D. Sendthe data to SQS for further processing.
Answer: ABC
Explanation:
Amazon Kinesis can be used for rapid and continuous data intake and aggregation. The type of data used includes IT infrastructure log data, application logs, social media, market data feeds, and web clickstream data Amazon Lambda is a web service which can be used to do serverless computing of the logs which are published by Cloudwatch logs Amazon dasticsearch Service makes it easy to deploy, operate, and scale dasticsearch for log analytics, full text search, application monitoring, and more.
For more information on Cloudwatch logs please see the below link: http://docs.ws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/logs/WhatlsCloudWatchLogs.html
NEW QUESTION 6
You need to create a simple, holistic check for your system's general availablity and uptime. Your system presents itself as an HTTP-speaking API. What is the most simple tool on AWS to achieve this with?
- A. Route53 Health Checks
- B. CloudWatch Health Checks
- C. AWS ELB Health Checks
- D. EC2 Health Checks
Answer: A
Explanation:
Amazon Route 53 health checks monitor the health and performance of your web applications, web servers, and other resources. Each health check that you create
can monitor one of the following:
• The health of a specified resource, such as a web server
• The status of an Amazon Cloud Watch alarm
• The status of other health checks
For more information on Route53 Health checks, please refer to the below link:
• http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/dns-fa ilover.html
NEW QUESTION 7
You currently have an application deployed via Elastic Beanstalk. You are now deploying a new application and have ensured that Elastic beanstalk has detached the current instances and deployed and reattached new instances. But the new instances are still not receiving any sort of traffic. Why is this the case.
- A. The instances are of the wrong AMI, hence they are not being detected by the ELB.
- B. It takes time for the ELB to register the instances, hence there is a small timeframe before your instances can start receiving traffic
- C. You need to create a new Elastic Beanstalk application, because you cannot detach and then reattach instances to an ELB within an Elastic Beanstalk application
- D. The instances needed to be reattached before the new application version was deployed
Answer: B
Explanation:
Before the CC2 Instances can start receiving traffic, they will be checked via the health checks of the CLB. Once the health checks are successful, the CC2 Instance
will change its state to InService and then the EC2 Instances can start receiving traffic. For more information on ELB health checks, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/elb-healthchecks.html
NEW QUESTION 8
After a daily scrum with your development teams, you've agreed that using Blue/Green style deployments would benefit the team. Which technique should you use to deliver this new requirement?
- A. Re-deploy your application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and take advantage of Elastic Beanstalk deployment types.
- B. Using an AWS CloudFormation template, re-deploy your application behind a load balancer, launch a new AWS CloudFormation stack during each deployment, update your load balancer to send half your traffic to the new stack while you test, after verification update the load balancer to send 100% of traffic to the new stack, and then terminate the old stack.
- C. Create a new Autoscaling group with the new launch configuration and desired capacity same as that of the initial Autoscaling group andassociate it with the same load balance
- D. Once the new AutoScaling group's instances got registered with ELB, modify the desired capacity of the initial AutoScal ing group to zero and gradually delete the old Auto scaling grou
- E. •>/
- F. Using an AWS OpsWorks stack, re-deploy your application behind an Elastic Load Balancing load balancer and take advantage of OpsWorks stack versioning, during deployment create a new version of your application, tell OpsWorks to launch the new version behind your load balancer, and when the new version is launched, terminate the old OpsWorks stack.
Answer: C
Explanation:
This is given as a practice in the Green Deployment Guides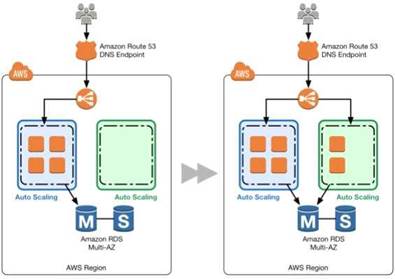
A blue group carries the production load while a green group is staged and deployed with the new code. When if s time to deploy, you simply attach the green group to
the existing load balancer to introduce traffic to the new environment. For HTTP/HTTP'S listeners, the load balancer favors the green Auto Scaling group because it uses a least outstanding requests routing algorithm
As you scale up the green Auto Scaling group, you can take blue Auto Scaling group instances out of service by either terminating them or putting them in Standby state.
For more information on Blue Green Deployments, please refer to the below document link: from AWS
https://dOawsstatic.com/whitepapers/AWS_Blue_Green_Deployments.pdf
NEW QUESTION 9
Which of the following is not a supported platform for the Elastic beanstalk service
- A. Java
- B. AngularJS
- C. PHP
- D. .Net
Answer: B
Explanation: 
For more information on Elastic beanstalk, please visit the below URL:
http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/concepts.platforms. htm I
NEW QUESTION 10
For AWS Auto Scaling, what is the first transition state an instance enters after leaving steady state when scaling in due to health check failure or decreased load?
- A. Terminating
- B. Detaching
- C. Terminating:Wait
- D. EnteringStandby
Answer: A
Explanation:
The below diagram shows the Lifecycle policy. When the scale-in happens, the first action is the Terminating action.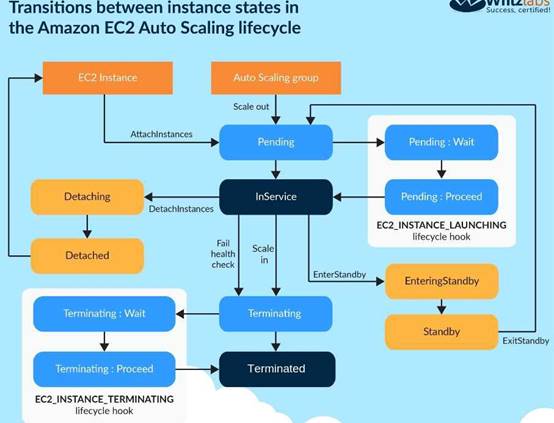
For more information on Autoscaling Lifecycle, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/AutoScaingGroupLifecycle.html
NEW QUESTION 11
A user is using Cloudformation to launch an EC2 instance and then configure an application after the instance is launched. The user wants the stack creation of ELB and AutoScaling to wait until the EC2 instance is launched and configured properly. How can the user configure this?
- A. It is not possible that the stackcreation will wait until one service is created and launchedB.The user can use theHoldCondition resource to wait for the creation of the other dependent resources
- B. The user can use theDependentCondition resource to hold the creation of the other dependentresources
- C. The user can use the WaitConditionresource to hold the creation of the other dependent resources
Answer: D
Explanation:
You can use a wait condition for situations like the following:
To coordinate stack resource creation with configuration actions that are external to the stack creation
To track the status of a configuration process
For more information on Cloudformation Wait condition please visit the link
http://docs^ws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-properties-waitcondition.htmI
NEW QUESTION 12
You are using Chef in your data center. Which service is designed to let the customer leverage existing Chef recipes in AWS?
- A. AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- B. AWSOpsWorks
- C. AWS CloudFormation
- D. Amazon Simple Workflow Service
Answer: B
Explanation:
AWS OpsWorks is a configuration management service that uses Chef, an automation platform that treats server configurations as code. OpsWorks uses Chef to
automate how servers are configured, deployed, and managed across your Amazon Clastic Compute Cloud (Amazon CC2) instances or on-premises compute
environments. OpsWorks has two offerings, AWS Opsworks for Chef Automate, and AWS OpsWorks Stacks.
For more information on Opswork and SNS please refer to the below link:
• https://aws.amazon.com/opsworks/
NEW QUESTION 13
You have an application running a specific process that is critical to the application's functionality, and have added the health check process to your Auto Scaling Group. The instances are showing healthy but the application itself is not working as it should. What could be the issue with the health check, since it is still showing the instances as healthy.
- A. You do not have the time range in the health check properly configured
- B. It is not possible for a health check to monitor a process that involves the application
- C. The health check is not configured properly
- D. The health check is not checking the application process
Answer: D
Explanation:
If you have custom health checks, you can send the information from your health checks to Auto Scaling so that Auto Scaling can use this information. For example, if
you determine that an instance is not functioning as expected, you can set the health status of the instance to Unhealthy. The next time that Auto Scaling performs a
health check on the instance, it will determine that the instance is unhealthy and then launch a replacement instance
For more information on Autoscaling health checks, please refer to the below document link: from AWS
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/healthcheck.html
NEW QUESTION 14
What are the benefits when you implement a Blue Green deployment for your infrastructure or application level changes. Choose 3 answers from the options given below
- A. Nearzero-downtime release for new changes
- B. Betterrollback capabilities
- C. Abilityto deploy with higher risk
- D. Goodturnaround time for application deployments
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
Blue/green deployments provide near zero-downtime release and rollback capabilities. The fundamental idea behind blue/green deployment is to shift traffic between two identical environments that are running different versions of your application. The blue environment represents the current application version serving production traffic. In parallel, the green environment is staged running a different version of your application. After the green environment is ready and tested, production traffic is redirected from blue to green.
For more information on Blue Green deployments please see the below link:
• https://dOawsstatic.com/whitepapers/AWS_Blue_Green_Deployments.pdf
NEW QUESTION 15
When one creates an encrypted EBS volume and attach it to a supported instance type ,which of the following data types are encrypted?
Choose 3 answers from the options below
- A. Dataat rest inside the volume
- B. Alldata copied from the EBS volume to S3
- C. Alldata moving between the volume and the instance
- D. Allsnapshots created from the volume
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
This is clearly given in the aws documentation. Amazon EBS Encryption
Amazon CBS encryption offers a simple encryption solution for your CBS volumes without the need to build, maintain, and secure your own key management infrastructure. When you create an encrypted CBS volume and attach it to a supported instance type, the following types of data are encrypted:
• Data at rest inside the volume
• All data moving between the volume and the instance
• All snapshots created from the volume
• All volumes created from those snapshots
For more information on CBS encryption, please refer to the below url http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/AWSCC2/latest/UserGuide/CBSCncryption.html
NEW QUESTION 16
You currently have an Autoscalinggroup that has the following settings Min capacity-2
Desired capacity - 2 Maximum capacity - 2
Your launch configuration has AMI'S which are based on the t2.micro instance type. The application running on these instances are now experiencing issues and you have identified that the solution is to change the instance type of the instances running in the Autoscaling Group.
Which of the below solutions will meet this demand.
- A. Change the Instance type in the current launch configuratio
- B. Change the Desired value of the Autoscaling Group to 4. Ensure the new instances are launched.
- C. Delete the current Launch configuratio
- D. Create a new launch configuration with the new instance type and add it to the Autoscaling Grou
- E. This will then launch the new instances.
- F. Make a copy the Launch configuratio
- G. Change the instance type in the new launch configuratio
- H. Attach that to the Autoscaling Group.Change the maximum and Desired size of the Autoscaling Group to 4. Once the new instances are launched, change the Desired and maximum size back to 2.
- I. Change the desired and maximum size of the Autoscaling Group to 4. Make a copy the Launch configuratio
- J. Change the instance type in the new launch configuratio
- K. Attach that to the Autoscaling Grou
- L. Change the maximum and Desired size of the Autoscaling Group to 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
You should make a copy of the launch configuration, add the new instance type. The change the Autoscaling Group to include the new instance type. Then change the Desired number of the Autoscaling Group to 4 so that instances of new instance type can be launched. Once launched, change the desired size back to 2, so that Autoscaling will delete the instances with the older configuration. Note that the assumption here is that the current instances are equally distributed across multiple AZ's because Autoscaling will first use the AZRebalance process to terminate instances.
Option A is invalid because you cannot make changes to an existing Launch configuration.
Option B is invalid because if you delete the existing launch configuration, then your application will not be available. You need to ensure a smooth deployment process.
Option D is invalid because you should change the desired size to 4 after attaching the new launch configuration.
For more information on Autoscaling Suspend and Resume, please visit the below URL: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/as-suspend-resu me-processes.html
NEW QUESTION 17
You need to perform ad-hoc analysis on log data, including searching quickly for specific error codes and reference numbers. Which should you evaluate first?
- A. AWS Elasticsearch Service
- B. AWSRedShift
- C. AWSEMR
- D. AWSDynamoDB
Answer: A
Explanation:
Amazon Dasticsearch Service makes it easy to deploy, operate, and scale dasticsearch for log analytics, full text search, application monitoring, and more. Amazon
Oasticsearch Service is a fully managed service that delivers Dasticsearch's easy-to-use APIs and real- time capabilities along with the availability, scalability, and security required by production workloads. The service offers built-in integrations with Kibana, Logstash, and AWS services including Amazon Kinesis Firehose, AWS Lambda, and Amazon CloudWatch so that you can go from raw data to actionable insights quickly For more information on the elastic cache service, please refer to the below link:
• https://aws.amazon.com/elasticsearch-service/
NEW QUESTION 18
Which of the following features of the Elastic Beanstalk service will allow you to perform a Blue Green Deployment
- A. Rebuild Environment
- B. Swap Environment
- C. Swap URL's
- D. Environment Configuration
Answer: C
Explanation:
With the Swap url feature, you can keep a version of your environment ready. And when you are ready to cut over, you can just use the swap url feature to switch over
to your new environment
For more information on swap url feature, please refer to the below link:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/using-features.CNAMCSwap.html
NEW QUESTION 19
You work at a company that makes use of AWS resources. One of the key security policies is to ensure that all data is encrypted both at rest and in transit. Which of the following is not a right implementation which aligns to this policy?
- A. UsingS3 Server Side Encryption (SSE) to store the information
- B. Enable SSLtermination on the ELB C EnablingProxy ProtocolD- Enablingsticky sessions on your load balancer
Answer: B
Explanation:
Please note the keyword "NOT" in the question.
Option A is incorrect. Enabling S3 SSE encryption helps the encryption of data at rest in S3.So Option A is invalid.
Option B is correct. If you disable SSL termination on the ELB the traffic will be encrypted all the way to the backend. SSL termination allows encrypted traffic between the client
and the ELB but cause traffic to be unencrypted between the ELB and the backend (presumably EC2 or ECS/Task, etc.)
If SSL is not terminated on the ELB you must use Layer A to have traffic encrypted all the way.
Sticky sessions are not supported with Layer A (TCP endpoint). Thus option D" Enabling sticky sessions on your load balancer" can't be used and is the right answer
For more information on sticky sessions, please visit the below URL https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/elb-sticky-sessions.html Requirements
• An HTTP/HTTPS load balancer.
• At least one healthy instance in each Availability Zone.
• At least one healthy instance in each Availability Zone.
If you don't want the load balancer to handle the SSL termination (known as SSL offloading), you can use TCP for both the front-end and back-end connections, and deploy certificates on the registered instances handling requests.
For more information on elb-listener-config, please visit the below
• https://docs.awsamazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/elb-listener-config.html If the front-end connection uses TCP or SSL, then your back-end connections can use either TCP or SSL. Note: You can use an HTTPS listener and still use SSL on the backend but the ELB must terminate, decrypt and re-encrypt. This is slower and less secure then using the same encryption all the way to the backend.. It also breaks the question requirement of having all data encrypted in transit since it force the ELB to decrypt Proxy protocol is used to provide a secure transport connection hence Option C is also incorrect. For more information on SSL Listeners for your load balancer, please visit the below URL
http://docsaws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/elb-https-load-balancers.html
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/elastic-load-balancer-support-for-ssl-termination/
NEW QUESTION 20
You have deployed an application to AWS which makes use of Autoscaling to launch new instances. You now want to change the instance type for the new instances. Which of the following is one of the action items to achieve this deployment?
- A. Use Elastic Beanstalk to deploy the new application with the new instance type
- B. Use Cloudformation to deploy the new application with the new instance type
- C. Create a new launch configuration with the new instance type
- D. Create new EC2 instances with the new instance type and attach it to the Autoscaling Group
Answer: C
Explanation:
The ideal way is to create a new launch configuration, attach it to the existing Auto Scaling group, and terminate the running instances.
Option A is invalid because Clastic beanstalk cannot launch new instances on demand. Since the current scenario requires Autoscaling, this is not the ideal option
Option B is invalid because this will be a maintenance overhead, since you just have an Autoscaling Group. There is no need to create a whole Cloudformation
template for this.
Option D is invalid because Autoscaling Group will still launch CC2 instances with the older launch configuration
For more information on Autoscaling Launch configuration, please refer to the below document link: from AWS
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/l_aunchConfiguration.html
NEW QUESTION 21
You are Devops Engineer for a large organization. The company wants to start using Cloudformation templates to start building their resources in AWS. You are getting requirements for the templates from various departments, such as the networking, security, application etc. What is the best way to architect these Cloudformation templates.
- A. Usea single Cloudformation template, since this would reduce the maintenanceoverhead on the templates itself.
- B. Createseparate logical templates, for example, a separate template for networking,security, application et
- C. Then nest the relevant templates.
- D. Considerusing Elastic beanstalk to create your environments since Cloudformation is notbuilt for such customization.
- E. Considerusing Opsworks to create your environments since Cloudformation is not builtfor such customization.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS documentation mentions the following
As your infrastructure grows, common patterns can emerge in which you declare the same components in each of your templates. You can separate out these
common components and create dedicated templates for them. That way, you can mix and match different templates but use nested stacks to create a single, unified stack. Nested stacks are stacks that create other stacks. To create nested stacks, use the AWS::
Cloud Form ation::Stackresource in your template to reference other templates.
For more information on Cloudformation best practises, please visit the below url http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
NEW QUESTION 22
Which of the following credentials types are supported by AWSCodeCommit? Select 3 Options
- A. Git Credentials
- B. SSH Keys
- C. User name/password
- D. AWS Access Kevs
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
The AWS documentation mentions
I AM supports AWS CodeCommit with three types of credentials:
Git credentials, an 1AM -generated user name and password pair you can use to communicate with AWS CodeCommit repositories over HTTPS.
SSH keys, a locally generated public-private key pair that you can associate with your 1AM user to communicate with AWS CodeCommit repositories over SSH.
AWS access keys, which you can use with the credential helper included with the AWS CLI to communicate with AWS CodeCommit repositories over HTTPS. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_ssh-keys.htmI
NEW QUESTION 23
......
P.S. Easily pass DOP-C01 Exam with 116 Q&As Allfreedumps.com Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest Allfreedumps.com DOP-C01 Dumps: https://www.allfreedumps.com/DOP-C01-dumps.html (116 New Questions)