Your success in Cisco 200-105 is our sole target and we develop all our 200-105 braindumps in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our 200-105 study material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. 200-105 Practice Exams for Cisco 200-105 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Also have 200-105 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which command do you enter to view EIGRPv6 adjacencies?
- A. show ipv6 eigrp 1 interface
- B. show ipv6 route eigrp
- C. show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
- D. show running-configuration eigrp
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 2
Which three checks must you perform when troubleshooting EIGRPvB adjacencies? (Choose three.)
- A. Verify that IPv6 is enabled.
- B. Verify that the network command has been configured.
- C. Verify that auto summary is enabled.
- D. Verify that the interface is up.
- E. Verify that an IPv4 address has been configured.
- F. Verify that the router ID has been configured.
Answer: ADF
NEW QUESTION 3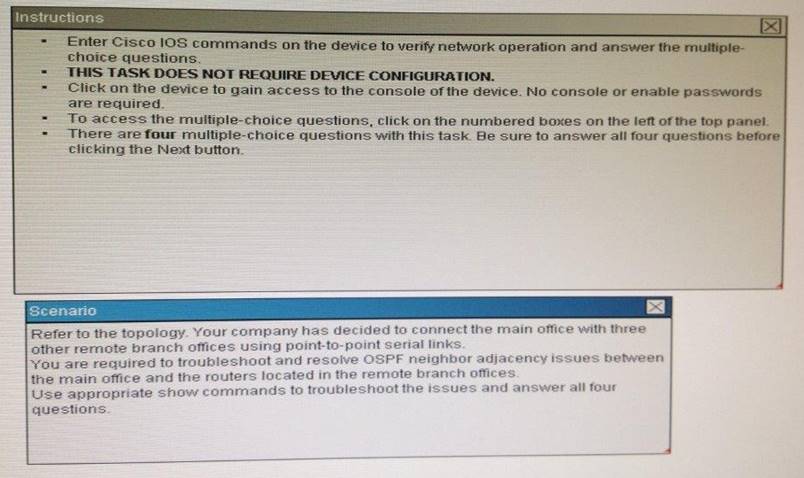
R1# show running-config interface Loopback0
description ***Loopback***
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
description **Connected to R1-LAN** ip address 10.10.110.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
description **Connected to L2SW**
ip address 10.10.230.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf hello-interval 25 ip ospf 1 area 0
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
R2# show running-config R2
!
interface Loopback0 description **Loopback**
ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 2 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
description **Connected to R2-LAN** ip address 10.10.120.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 2 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
description **Connected to L2SW**
ip address 10.10.230.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 2 area 0
!
router ospf 2
log-adjacency-changes
R3# show running-config R3
username R6 password CISCO36
!
interface Loopback0 description **Loopback**
ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 3 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
description **Connected to L2SW**
ip address 10.10.230.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 3 area 0
!
interface Serial1/0
description **Connected to R4-Branch1 office** ip address 10.10.240.1 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp ip ospf 3 area 0
!
interface Serial1/1
description **Connected to R5-Branch2 office** ip address 10.10.240.5 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp
ip ospf hello-interval 50 ip ospf 3 area 0
!
interface Serial1/2
description **Connected to R6-Branch3 office** ip address 10.10.240.9 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp ip ospf 3 area 0
ppp authentication chap
!
router ospf 3
router-id 192.168.3.3
!
R4# show running-config
R4
!
interface Loopback0 description **Loopback**
ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 4 area 2
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.16.113.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 4 area 2
!
interface Serial1/0
description **Connected to R3-Main Branch office** ip address 10.10.240.2 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp ip ospf 4 area 2
!
router ospf 4
log-adjacency-changes
R5# show running-config R5
!
interface Loopback0 description **Loopback**
ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 5 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.16.114.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 5 area 0
!
interface Serial1/0
description **Connected to R3-Main Branch office**
ip address 10.10.240.6 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp ip ospf 5 area 0
!
router ospf 5
log-adjacency-changes
R6# show running-config R6
username R3 password CISCO36
!
interface Loopback0 description **Loopback**
ip address 192.168.6.6 255.255.255.255
ip ospf 6 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.16.115.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 6 area 0
!
interface Serial1/0
description **Connected to R3-Main Branch office** ip address 10.10.240.10 255.255.255.252
encapsulation ppp ip ospf 6 area 0
ppp authentication chap
!
router ospf 6
router-id 192.168.3.3
!
R1 does not form an OSPF neighbor adjacency with R2. Which option would fix the issue?
- A. R1 ethernet0/1 is shutdow
- B. Configure the no shutdown command.
- C. R1 ethernet0/1 configured with a non-default OSPF hello interval of 25, configure no ip ospf hello interval 25
- D. R2 ethernet0/1 and R3 ethernet0/0 are configured with a non-default OSPF hello interval of 25; configure no ip ospf hello interval 25
- E. Enable OSPF for R1 ethernet0/1; configure ip ospf 1 area 0 command under ethernet0/1
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 4
How does a router handle an incoming packet whose destination network is missing from the Routing table?
- A. it discards the packet.
- B. it broadcasts the packet to each network on the router.
- C. it routes the packet to the default route.
- D. it broadcasts the packet to each interface on the router.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to Exhibit: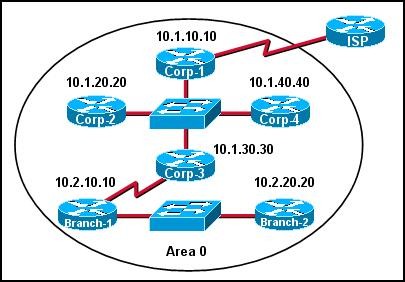
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance. As part of examining the router resources, the OSPF DRs need to be known. All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router. Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two.)
- A. Corp-1
- B. Corp-2
- C. Corp-3
- D. Corp-4
- E. Branch-1
- F. Branch-2
Answer: DF
Explanation:
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40)
& Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
NEW QUESTION 6
If host Z needs to send data through router R1 to a storage server, which destination MAC address does host Z use to transmit packets?
- A. the host Z MAC address
- B. the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to the storage server
- C. the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to host Z
- D. the MAC address of the storage server interface
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 7
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
- A. a backup route, stored in the routing table
- B. a primary route, stored in the routing table
- C. a backup route, stored in the topology table
- D. a primary route, stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f07.shtml
Feasible Successors
A destination entry is moved from the topology table to the routing table when there is a feasible successor. All minimum cost paths to the destination form a set. From this set, the neighbors that have an advertised metric less than the current routing table metric are considered feasible successors.
Feasible successors are viewed by a router as neighbors that are downstream with respect to the destination.
These neighbors and the associated metrics are placed in the forwarding table.
When a neighbor changes the metric it has been advertising or a topology change occurs in the network, the set of feasible successors may have to be re-evaluated. However, this is not categorized as a route recomputation.
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance (AD) is less than the Feasible Distance (FD) of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but, stored in the topology table.
NEW QUESTION 8
The command frame-relay map ip 10.121.16.8 102 broadcast was entered on the router. Which of the following statements is true concerning this command?
- A. This command should be executed from the global configuration mode.
- B. The IP address 10.121.16.8 is the local router port used to forward data.
- C. 102 is the remote DLCI that will receive the information.
- D. This command is required for all Frame Relay configurations.
- E. The broadcast option allows packets, such as RIP updates, to be forwarded across the PVC.
Answer: E
Explanation:
The command frame-relay map ip 10.121.16.8 102 broadcast means to map the remote IP 10.121.16.8 to the local DLCI 102. When the “broadcast” keyword is included, it turns Frame Relay network as a broadcast network, which can forward broadcasts.
NEW QUESTION 9
DRAG DROP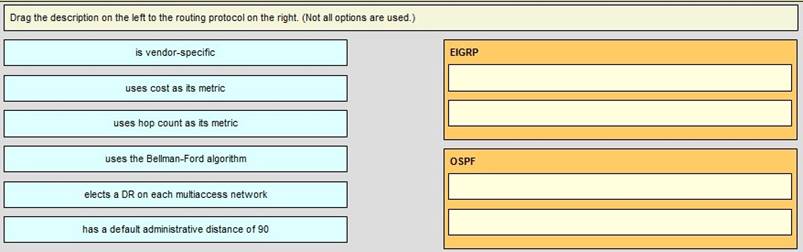
- A. Mastered
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
Explanation:
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol, so it is vendor-specific. By default, EIGRP internal routes have an administrative distance value of 90.
OSPF uses cost as its metric. By default, the cost of an interface is calculated based on bandwidth with the formula cost= 10000 0000/bandwidth (in bps). OSPF elects a DR on each broadcast and nonbroadcast multiaccess networks (like Ethernet and Frame Relay
environments, respectively). It doesn’t elect a DR on point-to-point link (like a serial WAN).
NEW QUESTION 10
Which command is used to enable CHAP authentication, with PAP as the fallback method, on a serial interface?
- A. Router(config-if)# ppp authentication chap fallback ppp
- B. Router(config-if)# ppp authentication chap pap
- C. Router(config-if)# authentication ppp chap fallback ppp
- D. Router(config-if)# authentication ppp chap pap
Answer: B
Explanation:
The command “ppp authentication chap pap” command indicates the CHAP authentication is used first. If it fails or is rejected by other side then uses PAP instead. If you want to use PAP first (then CHAP) you can use the “ppp authentication pap chap” command Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/security/configuration/guide/scfathen.html
NEW QUESTION 11
Refer to the exhibit.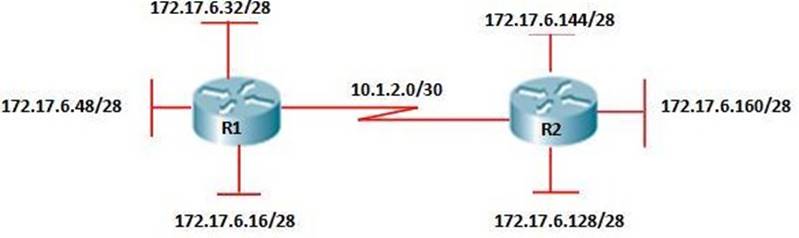

From R1, a network administrator is able to ping the serial interface of R2 but, unable to ping any of the subnets attached to RouterB. Based on the partial outputs in the exhibit, what could be the problem?
- A. EIGRP does not support VLSM.
- B. The EIGRP network statements are incorrectly configured.
- C. The IP addressing on the serial interface of RouterA is incorrect.
- D. The routing protocol has summarized on the classful boundary.
- E. EIGRP has been configured with an invalid autonomous system number.
Answer: D
Explanation:
CCNA - EIGRP Common Question Reference:
http://www.orbitco-ccna-pastquestions.com/CCNA---EIGRP-Common-Question.php
If you look carefully at the R2 ip route, you will discover that the R2 does not learn any network from R1; this is because the routing protocol used here (EIGRP) performs auto summary when advertising routes to peers across a network. So in this case the address 172.17.0.0/16 is a summarized address. If the router was configured with no auto summary command, R2 LAN addresses would have been advertised and reached.
NEW QUESTION 12
After you configure a GRE tunnel between two networks, the tunnel comes up normally, but workstations on each side of the tunnel cannot communicate. Which reason for the problem is most likely true?
- A. The tunnel source address is incorrect.
- B. The tunnel destination address is incorrect.
- C. The route between the networks is undefined.
- D. The IP MTU is incorrect.
- E. The distance configuration is missing.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 13
CORRECT TEXT
A new switch is being added to the River Campus LAN. You will work to complete this
process by first configuring the building_2 switch with an IP address and default gateway. For the switch host address, you should use the last available IP address on the management subnet. In addition, the switch needs to be configured to be in the same VTP domain as the building_1 switch and also needs to be configured as a VTP client. Assume that the IP configuration and VTP configuration on building_1 are complete and correct. The configuration of the router is not accessible for this exercise. You must accomplish the following tasks:
Determine and configure the IP host address of the new switch. Determine and configure the default gateway of the new switch. Determine and configure the correct VTP domain name for the new switch.
Configure the new switch as a VTP client.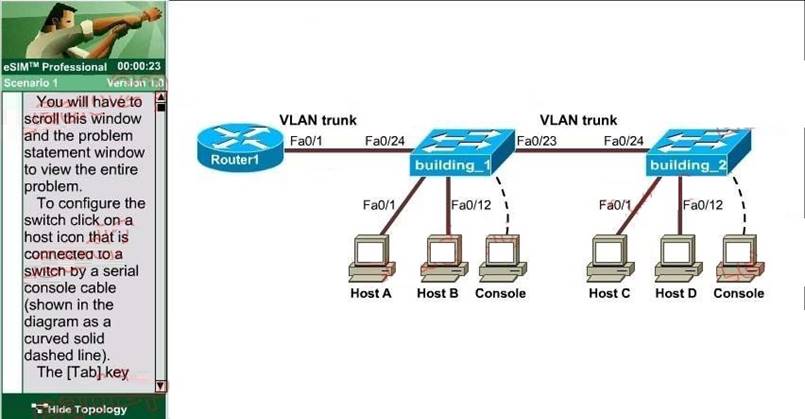
- A. Mastered
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
Explanation:
The question states we can't access the router so we can only get required information from switch building_1. Click on the PC connected with switch building_1 (through a console line) to access switch building_1s CLI. On this switch use the show running-config command:
building_1#show running-config
Next use the show vtp status command to learn about the vtp domain on this switch building_1#show vtp status
(Notice: the IP address, IP default-gateway and VTP domain name might be different!!!) You should write down these 3 parameters carefully.
Configuring the new switch
+ Determine and configure the IP host address of the new switch The question requires "for
the switch host address, you should use the last available IP address on the management subnet". The building_1 switch's IP address, which is 192.168.22.50 255.255.255.224, belongs to the management subnet.
Increment: 32 (because 224 = 1110 0000)
Network address: 192.168.22.32
Broadcast address: 192.168.22.63
->The last available IP address on the management subnet is 192.168.22.62 and it hasn't been used (notice that the IP address of Fa0/1 interface of the router is also the default gateway address 192.168.22.35).
Also notice that the management IP address of a switch should be configured in Vlan1 interface. After it is configured, we can connect to it via telnet or SSH to manage it. Switch2#configure terminal
Switch2(config)#interface Vlan1
Switch2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.22.62 255.255.255.224
Switch2(config-if)#no shutdown (not really necessary since VLAN interfaces are not physical and are not shut
down but, no harm in doing so and is good practice for physical ports)
+ Determine and configure the default gateway of the new switch The default gateway of this new switch is same as that of building_1 switch, which is 192.168.22.35 Switch2(config-if)#exit
Switch2(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.22.35
+ Determine and configure the correct VTP domain name for the new switch The VTP domain name shown on building_1 switch is Cisco so we have to use it in the new switch (notice: the VTP domain name will be different in the exam and it is case sensitive so be careful)
Switch2(config)#vtp domain Cisco
+ Configure the new switch as a VTP client Switch2(config)#vtp mode client
We should check the new configuration with the "show running-config" & "show vtp status"; also try pinging from the new switch to the the default gateway to make sure it works well. Finally save the configuration:
Switch2(config)#exit
Switch2#copy running-config startup-config
NEW QUESTION 14
Which process is associated with spanning-tree convergence?
- A. determining the path cost
- B. electing designated ports
- C. learning the sender bridge ID
- D. assigning the port ID
Answer: B
Explanation:
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) convergence (Layer 2 convergence) happens when bridges and switches have transitioned to either the forwarding or blocking state. When layer 2 is converged, Root Switch is elected and Root Ports, Designated Ports and Non-Designated ports in all switches are selected. At Converged condition, the Root Ports and the Designated ports are in forwarding state, and all other ports are in blocking state.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which statements are true about EIGRP successor routes? (Choose two.)
- A. A successor route is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to a destination.
- B. Successor routes are saved in the topology table to be used if the primary route fails.
- C. Successor routes are flagged as 'active' in the routing table.
- D. A successor route may be backed up by a feasible successor route.
- E. Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
Introduction to EIGRP
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f07.shtml
Feasible Successors
A destination entry is moved from the topology table to the routing table when there is a feasible successor. All minimum cost paths to the destination form a set. From this set, the neighbors that have an advertised metric less than the current routing table metric are considered feasible successors.
Feasible successors are viewed by a router as neighbors that are downstream with respect to the destination.
These neighbors and the associated metrics are placed in the forwarding table.
When a neighbor changes the metric it has been advertising or a topology change occurs in the network, the set of feasible successors may have to be re-evaluated. However, this is not categorized as a route recomputation.
NEW QUESTION 16
What is the result of issuing the frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.2 202 broadcast command?
- A. defines the destination IP address that is used in all broadcast packets on DCLI 202
- B. defines the source IP address that is used in all broadcast packets on DCLI 202
- C. defines the DLCI on which packets from the 192.168.1.2 IP address are received
- D. defines the DLCI that is used for all packets that are sent to the 192.168.1.2 IP address
Answer: D
Explanation:
Frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.2 202 command statically defines a mapping between a network layer address and a DLCI. The broadcast option allows multicast and broadcast packets to flow across the link.
The command frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.2 202 broadcast means to mapping the distal IP 192.168.1.2 202 to the local DLCI . When the “broadcast” keyword is included, it turns Frame Relay network as a broadcast network, which can forward broadcasts. http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/wan/command/reference/wan_f2.html#wp1012264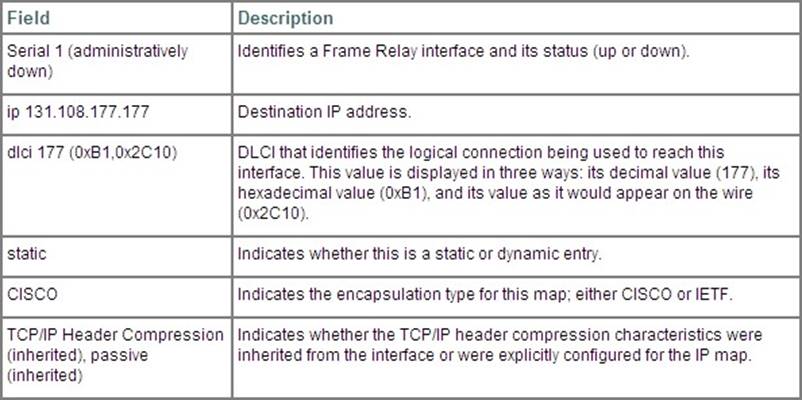
NEW QUESTION 17
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
- A. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
- B. Router# show ip eigrp topology
- C. Router#show ip eigrp interfaces
- D. Router#show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D
Explanation:
Implementing EIGRP http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1171169&seqNum=3
Below is an example of the show ip eigrp neighbors command. The retransmit interval (Smooth Round Trip Timer – SRTT) and the queue counts (Q count, which shows the number of queued EIGRP packets) for the adjacent routers are listed:
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num 0 10.10.10.2 Fa0/0 12 00:00:39 1282 5000 0 3
NEW QUESTION 18
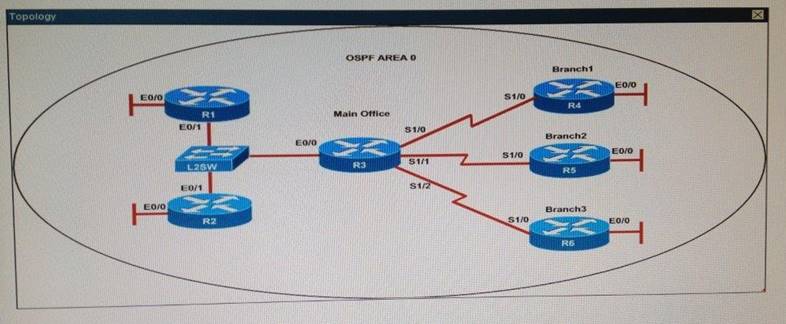
Scenario
Refer to the topology. Your company has connected the routers R1. R2. and R3 with serial links. R2 and R3 are connected to the switches SW1 and SW2, respectively. SW1 and SW2 are also connected to the routers R4 and R5.
The EIGRP routing protocol is configured.
You are required to troubleshoot and resolve the EIGRP issues between the various routers.
Use the appropriate show commands to troubleshoot the issues.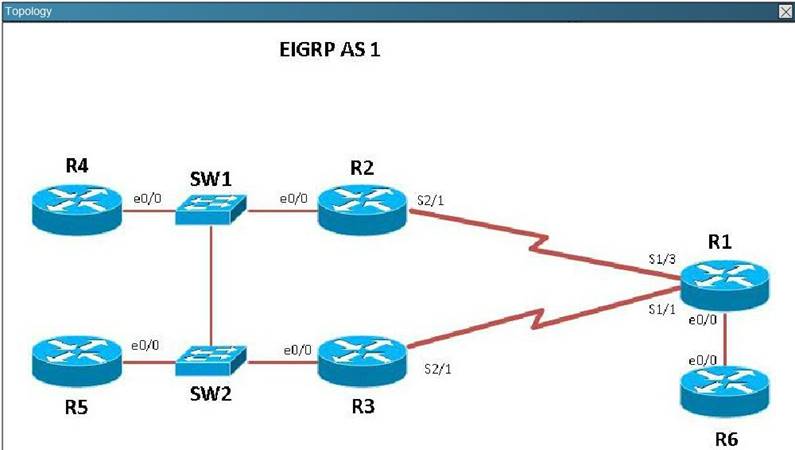





Study the following output taken on R1: R1# Ping 10.5.5.55 source 10.1.1.1 Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5.100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.5.5.55, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.1.1.1
Why are the pings failing?
- A. The network statement is missing on R5.
- B. The loopback interface is shut down on R5.
- C. The network statement is missing on R1.
- D. The IP address that is configured on the Lo1 interface on R5 is incorrect.
Answer: C
Explanation:
R5 does not have a route to the 10.1.1.1 network, which is the loopback0 IP address of R1. When looking at the EIGRP configuration on R1, we see that the 10.1.1.1 network statement is missing on R1.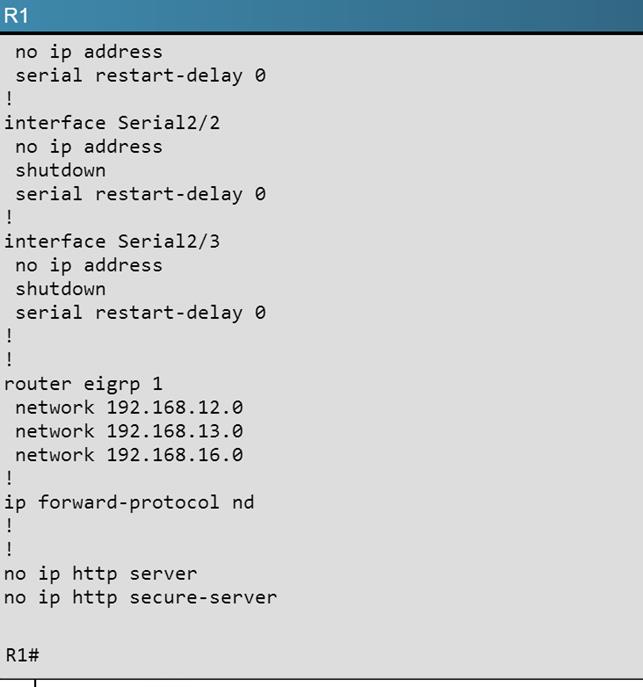
NEW QUESTION 19
When a router undergoes the exchange protocol within OSPF, in what order does it pass through each state?
- A. exstart state > loading state > exchange state > full state
- B. exstart state > exchange state > loading state > full state
- C. exstart state > full state > loading state > exchange state
- D. loading state > exchange state > full state > exstart state
Answer: B
Explanation:
OSPF states for adjacency formation are (in order) Down, Init, Attempt, 2-way, Exstart, Exchange, Loading and Full.
Reference:
Why Are OSPF Neighbors Stuck in Exstart/Exchange State? http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f0d.shtml
NEW QUESTION 20
Which feature can you implement to reserve bandwidth for voip calls across the call path?
- A. PQ
- B. Round Robin
- C. CBWFQ
- D. RSPV
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 21
Refer to the exhibit.
What is the meaning of the term dynamic as displayed in the output of the show frame- relay map command shown?
- A. The Serial0/0 interface is passing traffic.
- B. The DLCI 100 was dynamically allocated by the router
- C. The Serial0/0 interface acquired the IP address of 172.16.3.1 from a DHCP server
- D. The DLCI 100 will be dynamically changed as required to adapt to changes in the Frame Relay cloud
- E. The mapping between DLCI 100 and the end station IP address 172.16.3.1 was learned through Inverse ARP
Answer: E
Explanation:
The term dynamic indicates that the DLCI number and the remote router IP address
172.16.3.1 are learned via the Inverse ARP process.
Inverse ARP is a technique by which dynamic mappings are constructed in a network, allowing a device such as a router to locate the logical network address and associate it with a permanent virtual circuit (PVC).
NEW QUESTION 22
Which VLAN bridge priority value will make a switch as root for a given VLAN from the below options by the spanning-tree vlan vlan-id root command?
- A. 16384
- B. 8192
- C. 28672
- D. 32768
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 23
Refer to the exhibit.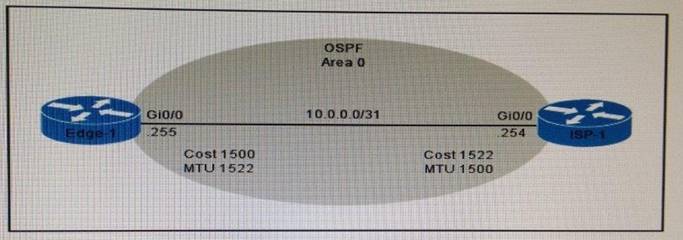
Router edge-1 is unable to establish OSPF neighbor adjacency with router ISP-1. Which
two configuration changes can you make on edge-1 to allow the two routers to establish adjacency? (Choose two.)
- A. Set the subnet mask on edge-1 to 255 255.255.252.
- B. Reduce the MTU on edge-1 to 1514.
- C. Set the OSPF cost on edge-1 to 1522.
- D. Reduce the MTU on edge-1 to 1500.
- E. Configure the ip ospf mtu-ignore command on the edge-1 Gi0/0 interface.
Answer: DE
Explanation:
A situation can occur where the interface MTU is at a high value, for example 9000, while the real value of the size of packets that can be forwarded over this interface is 1500.
If there is a mismatch on MTU on both sides of the link where OSPF runs, then the OSPF adjacency will not form because the MTU value is carried in the Database Description (DBD) packets and checked on the other side.
NEW QUESTION 24
Which Cisco platform can verify ACLs?
- A. Cisco Prime Infrastructure
- B. Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
- C. Cisco APIC-EM
- D. Cisco IOS-XE
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 25
The network administrator has been asked to give reasons for moving from IPv4 to IPv6. What are two valid reasons for adopting IPv6 over IPv4? (Choose two.)
- A. no broadcast
- B. change of source address in the IPv6 header
- C. change of destination address in the IPv6 header
- D. Telnet access does not require a password
- E. autoconfig
- F. NAT
Answer: AE
Explanation:
Six Benefits Of IPv6
http://www.networkcomputing.com/ipv6/six-benefits-of-ipv6/230500009
With IPv6, everything from appliances to automobiles can be interconnected. But an increased number of IT addresses isn't the only advantage of IPv6 over IPv4. In honor of World IPv6 Day, here are six more good reasons to make sure your hardware, software, and services support IPv6.
More Efficient Routing IPv6 reduces the size of routing tables and makes routing more efficient and hierarchical. IPv6 allows ISPs to aggregate the prefixes of their customers' networks into a single prefix and announce this one prefix to the IPv6 Internet. In addition, in IPv6 networks, fragmentation is handled by the source device, rather than the router, using a protocol for discovery of the path's maximum transmission unit (MTU).
More Efficient Packet Processing
IPv6's simplified packet header makes packet processing more efficient. Compared with IPv4, IPv6 contains no IP-level checksum, so the checksum does not need to be recalculated at every router hop. Getting rid of the IPlevel checksum was possible because most link-layer technologies already contain checksum and error-control capabilities. In addition, most transport layers, which handle end-to-end connectivity, have a checksum that enables error detection.
Directed Data Flows IPv6 supports multicast rather than broadcast. Multicast allows bandwidth-intensive packet flows (like multimedia streams) to be sent to multiple destinations simultaneously, saving network bandwidth.
Disinterested hosts no longer must process broadcast packets. In addition, the IPv6 header has a new field, named Flow Label, which can identify packets belonging to the same flow. Simplified Network Configuration Address auto-configuration (address assignment) is built in to IPv6. A router will send the prefix of the local link in its router advertisements. A host can generate its own IP address by appending its link-layer (MAC) address, converted into Extended Universal Identifier (EUI) 64-bit format, to the 64 bits of the local link prefix.
Support For New Services
By eliminating Network Address Translation (NAT), true end-to-end connectivity at the IP layer is restored, enabling new and valuable services. Peer-to-peer networks are easier to create and maintain, and services such as VoIP and Quality of Service (QoS) become more robust.
Security IPSec, which provides confidentiality, authentication and data integrity, is baked into in IPv6. Because of their potential to carry malware, IPv4 ICMP packets are often blocked by corporate firewalls, but ICMPv6, the implementation of the Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6, may be permitted because IPSec can be applied to the ICMPv6 packets.
NEW QUESTION 26
What does the frame-relay interface-dlci command configure?
- A. local DLCI on the subinterface
- B. remote DLCI on the main interface
- C. remote DCLI on the subinterface
- D. local DLCI on the main interface
Answer: A
Explanation:
Frame Relay for ICND Exam http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=100603&seqNum=3
To assign a data-link connection identifier (DLCI) to a specified Frame Relay subinterface on the router or access server, or to assign a specific permanent virtual circuit (PVC) to a DLCI, or to apply a virtual template configuration for a PPP session, use the frame-relay interface-dlci interface configuration command
Example 4-23 Example of frame-relay interface-dlci Command and the Output of show frame-relay map
R4(config)#interface s1/2.403 point-to-point R4(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci ?
<16-1007> Define a switched or locally terminated DLCI R4(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 403 ?
cisco Use CISCO Encapsulation
ietf Use RFC1490/RFC2427 Encapsulation
ppp Use RFC1973 Encapsulation to support PPP over FR protocol Optional protocol information for remote end
<cr>
R4#show frame-relay map
Serial1/2.403 (up): point-to-point dlci, dlci 403(0xC9,0x3090), broadcast status defined, active
R4#
NEW QUESTION 27
Which form of NAT maps multiple private IP addresses to a single registered IP address by using different
ports?
- A. static NAT
- B. dynamic NAT
- C. overloading
- D. overlapping
- E. port loading
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 28
What are two drawbacks of implementing a link-state routing protocol? (Choose two.)
- A. the sequencing and acknowledgment of link-state packets
- B. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality
- C. the high volume of link-state advertisements in a converged network
- D. the high demand on router resources to run the link-state routing algorithm
- E. the large size of the topology table listing all advertised routes in the converged network
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Link State routing protocols, such as OSPF and IS-IS, converge more quickly than their distance vector routing protocols such as RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP and so on, through the use of flooding and triggered updates. In link state protocols, changes are flooded immediately
and computed in parallel. Triggered updates improve convergence time by requiring routers to send an update message immediately upon learning of a route change. These updates are triggered by some event, such as a new link becoming available oor an existing link failing. The main drawbacks to link state routing protocols are the amount of CPU overhead involved in calculating route changes and memory resources that are required to store neighbor tables, route tables and a complete topology table. http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=24090&seqNum=4
NEW QUESTION 29
Which routing protocols are compatible with stubs. (Choose two)
- A. OSPF
- B. EIGRP
- C. EGP
- D. BGP
- E. IS_IS
- F. RIP
Answer: AB
NEW QUESTION 30
Which two statistics appear in show frame-relay map output? (Choose two.)
- A. the number of BECN packets that are received by the router
- B. the value of the local DLCI
- C. the number of FECN packets that are received by the router
- D. the status of the PVC that is configured on the router
- E. the IP address of the local router
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Frame Relay Commands (map-class frame-relay through threshold ecn) http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/wan/command/reference/wrffr4.html#wp102934 3
Examples
The following is sample output from the show frame-relay map command: Router#show frame-relay map Serial 1 (administratively down): ip 10.108.177.177 dlci 177 (0xB1,0x2C10), static, broadcast,
CISCO
TCP/IP Header Compression (inherited), passive (inherited)
NEW QUESTION 31
......
P.S. 2passeasy now are offering 100% pass ensure 200-105 dumps! All 200-105 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/200-105/ (267 New Questions)