Exam Code: 300-320 (Practice Exam Latest Test Questions VCE PDF)
Exam Name: Designing Cisco Network Service Architectures
Certification Provider: Cisco
Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass 300-320 Exam.
Check 300-320 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
What is the next action taken by the Cisco NAC Appliance after it identifies vulnerability on a client device?
- A. Denies the client network resource access
- B. Repairs the effected devices
- C. Generates a Syslog message
- D. Permits the client but limits to guest access
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Cisco NAC Appliance (formerly Cisco Clean Access) is a product that allows network administrators to authenticate, authorize, evaluate, and remediate wired, wireless, and remote users and their machines prior to allowing users onto the network. It identifies whether networked devices such as laptops, IP phones, personal digital assistants, or printers are compliant with an organization's security policies, and repairs any vulnerabilities before permitting access to the network. NAC Appliance lets you block access or quarantine users who do not comply with your security requirements, NAC Appliance enforces security policies by blocking, isolating, and repairing noncompliant machines in a quarantine area without needing administrator attention. Quarantining allows remediation servers to provide operating system patches and updates, virus definition files, or endpoint security solutions to compromised or vulnerable devices. Since there is no any word regarding quarantine in option B, denying access to clients would be the next action by NAC Appliance.
NEW QUESTION 2
How does OTV provide STP isolation?
- A. By using STP root optimization
- B. By using BPDU guard
- C. By dropping BPDU packets
- D. By using BPDU filtering
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 3
Which option lists the EIGRP minimum timer settings for hello and dead timers in seconds?
- A. 4 and 6
- B. 2 and 4
- C. 2 and 6
- D. Both 6
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 4
How does stub routing affect transit route in EIGRP?
- A. Transit routes are passed from a stub network to a hub network
- B. It prevents the hub router from advertising networks learned from the spoke
- C. Transit routes are filtered from stub networks to the network hub
- D. It’s designed to prevent the distribution of external routes
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 5
NAC: Simple access control at user and device contextual level. Which features are needed ? (Choose Two)
- A. secure access control
- B. TrustSec
- C. ISE
- D. NAC agent
Answer: CD
NEW QUESTION 6
Two Cisco switches with 1 SUP and many 10G line-card ports for each switch, run in VSS mode. In which case or for what reason you don't connect all VSL to SUP?
- A. The need for hardware diversity
- B. Bandwidth congestion at SUP
- C. In case the sup fail
- D. Qos must be configured on both
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
An engineer must optimize a single-homed connection in a small branch office. Which technology accomplishes this goal?
- A. MSE
- B. WAE
- C. DMVPN
- D. MPLS
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 8
After an incident caused by a DDOS attack on a router, an engineer must ensure that the router is accessible and protected from future attacks without making any changes to traffic passing through the router. Which security function can be utilized to protect the router?
- A. zone-based policy firewall
- B. access control lists
- C. class maps
- D. control plane policing
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 9
Which Cisco feature can be run on a Cisco router that terminates a WAN connection, to gather and provide WAN circuit information that helps switchover to dynamically back up the WAN circuit?
- A. Cisco Express Forwarding
- B. IP SLA
- C. Passive interface
- D. Traffic shaping
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 10
Which Cisco NAC Appliance design is the most scalable in large Layer 2-to-distribution implementation?
- A. Layer 2 out-of-band
- B. Layer 2 in-band
- C. Layer 3 out-of-band
- D. Layer 3 in-band
Answer: B
Explanation:
https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/foundation-learning-guide/9780132652933/ch08.html "Layer 2 In-Band Designs The Layer 2 in-band topology is the most common deployment option.
[...]
This is the most scalable design in large L2-to-distribution environments, because this design can be transparently implemented in the existing network supporting multiple access layer switches. It supports all
network infrastructure equipment. The Cisco NAS supports per-user ACLs."
NEW QUESTION 11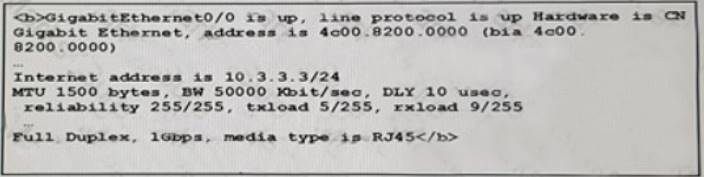
What should be implemented to prevent exceeding the 50mb allowable bandwidth of internet circuit?
- A. policing
- B. shaping
- C. CIR
- D. rate-limit
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 12
An engineer must design a Cisco VSS-based configuration within a customer campus network. The two VSS switches are provisioned for the campus distribution layer and each one has a single supervisor and multiple 10 gigabit line cards. Which option is the primary reason to avoid plugging both VSL links into the supervisor ports?
- A. The implementation creates a loop
- B. The design lacks optimal hardware diversity
- C. Limited bandwidth is available for VSS convergence
- D. QoS is required on the VSL links
Answer: B
Explanation:
The best-practice recommendation for VSL link resiliency is to bundle two 10-Gbps ports from different sources. Doing this might require having one port from the supervisor and other from a Cisco 6708 line card.
When configuring the VSL, note the following guidelines and restrictions:
For line redundancy, we recommend configuring at least two ports per switch for the VSL. For module redundancy, the two ports can be on different switching modules in each chassis.
NEW QUESTION 13
What are the two main characteristic of 802.1x (choose 2)
- A. EAP messages in Ethernet frames and don't use PPP
- B. works only on wired connections
- C. It's created by IETF
- D. It's created by IEEE
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 14
Which option is correct when using Virtual Switching System?
- A. Both control planes forward traffic simultaneously
- B. Only the active switch forward traffic
- C. Both data planes forward traffic simultaneously
- D. Only the active switch handles the control plane
Answer: C
Explanation:
Definitely C – again Chapter 1 of CiscoPress CCDP fourth edition Distribution-to Distribution Interconnect with the Virtual Switch Model
The virtual switch system operates differently at different planes. From a control plane point of view, the VSS peers (switches) operate in active standby redundancy mode. The switch in active redundancy mode will maintain the single configuration file for the VSS and sync it to the standby switch, and only the console interface on the active switch is accessible
VSS1440 (in the book) A VSS1440 refers to the VSS formed by two Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches with the Virtual Switching Supervisor 720-10GE. In a VSS, the data plane and switch fabric with capacity of 720 Gbps of supervisor engine in each chassis are active at the same time on both chassis, combining for an active 1400- Gbps switching capacity per VSS. Only one of the virtual switch members has the active control plane. Both chassis are kept in sync with the inter-chassis Stateful Switchover (SSO) mechanism along with Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) to provide nonstop communication even in the event of failure of one of the member supervisor engines or chassis.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/catalyst-6500-virtual-switchingsystem-
1440/prod_qas0900aecd806ed74b.html In my opinion C & D are correct.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which three statements about 802.1X are true? (Choose three)
- A. It is IEEE standard
- B. It can allow and deny port access based on device identity
- C. It works only with wired devices
- D. It can allow and deny port access based on user identity
Answer: ABD
NEW QUESTION 16
IP multicast packets when designing IPSec VPN?
- A. IPSec forwarding using tunnel mode
- B. Encapsulation of trafic with GRE or VTI
- C. Additional bandwidth for headend
- D. IPSec forwarding using transport mode
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 17
What command essentially turns on auto summarization for EIGRP?
- A. area 0 range 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0.0
- B. router eigrp 1
- C. ip summary-address eigrp 1 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
- D. ip summary-address 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
- E. eigrp stub
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 18
A link state routing protocol wants to connect tow separate domains, what should be configured (it's a question about IS-IS)?
- A. Level 1 router
- B. Level 1 router interface
- C. Level 2 router interface
- D. Level 2 router
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 19
A customer would like to implement a firewall to secure an enterprise network. However, the customer is unable to allocate any new subnets. What type of firewall mode must be implemented?
- A. routed
- B. active/standby
- C. transparent
- D. virtual
- E. active/active
- F. zone based
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 20
What is advantage of using the vPC feature in Data Centre environment?
- A. Two switches form a single control plane
- B. Utilizes all available uplinks bandwidth
- C. FHRP is not required
- D. A single IP is used for management for both devices
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 21
What are the two methods of ensuring that the RPF check passes? (Choose two)
- A. implementing static mroutes
- B. implementing OSPF routing protocol
- C. implementing MBGP
- D. disabling the interface of the router back to the multicast source
- E. disabling BGP routing protocol
Answer: AC
Explanation:
The router determines the RPF interface by the underlying unicast routing protocol or the dedicated multicast routing protocol in cases where one exists. An example of a dedicated multicast routing protocol is MP-BGP.
It is important to note that the multicast routing protocol relies on the underlying unicast routing table. Any change in the unicast routing table immediately triggers an RPF recheck on most modern routers. Having OSPF routing protocol in place won’t really ensure that the RPF check passes.
Let’s say we have implemented OSPF routing protocol within the topology below (have a look at the URL below), “R3” knows the best path to 1.1.1.0/24 is via interface F0/0 but “R3” receives multicast packet from source server (1.1.1.1/24) on interface S0/0. The RPF will fail. We can get this fixed by implementing static
mroutes (static multicast-routes) to force multicast traffic to go back via interface S0/0 (ip mroute 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0)
Having unicast routing protocol (OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, RIP, IGRP, IS-IS etc) won't necessarily mean the RPF will succeed but having a multicast routing protocol (Multipoint BGP) or dedicated multicast static routes (mroutes) will. The only which I still have is that if the multicast
routing protocol relies on the underlying unicast routing table (OSPF) how does it ensure that the RPF check passes.
https://supportforums.cisco.com/t5/network-infrastructure-documents/multicast-rpf-recovery-using-staticmultica routing/ta-p/3139007
NEW QUESTION 22
A network engineer wants to connect two sites via a WAN technology and to securely pass multicast traffic over this WAN technology. Which WAN technology should be configured?
- A. IPsec
- B. GRE
- C. Pure MPLS
- D. GRE over IPsec
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 23
What is the primary benefit of deployment MPLS over the WAN as opposed to extending VRF-lite across the WAN?
- A. convergence time
- B. low operating expense (OpEx)
- C. low latency
- D. dynamic fault-tolerance
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 24
An engineer wants to implement a network with the RSTP+ but the majority of the equipment is running STP. What will be the outcome when running STP and RSTP+ simultaneously?
- A. RSTP and STP will not work and the interface will be in error disabled
- B. RSTP and STP will work and fast convergence will happen
- C. RSTP and STP will work and fast convergence will not happen
- D. RSTP and STP will choose the best convergence protocol
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 25
What is the primary benefit of deployment MPLS over the WAN as opposed to extending VRF-lite across the WAN?
- A. Convergence time
- B. Low operating expense (OpEx)
- C. Low latency
- D. Dynamic fault-tolerance
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 26
A Network administrator want to increase the security level in the core layer and want to confirm that the users that have their default GW on an interface in the core switch can access specific networks and can’t access the remaining networks. Which feature can help him to achieve this?
- A. vlan access control list
- B. …
- C. …
- D. …
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 27
HSRP. Router 1 (master) and Router 2 (standby), same priority. When router 1 f0/1 (outside interface) down. With which tracking commands the Router 2 will be able to preempt ? (Choose Two)
- A. Track 50
- B. Track 50 decrement 20
- C. ip tracking 50 interface f0/1 reachability
- D. ip tracking 50 Interface f0/1 ip routing (or line protocol)
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 28
An engineer has implemented a QoS architecture that requires a signalling protocol to tell routers which flows of packets require special treatment. Which two mechanisms are important to establish and maintaining QoS architecture? (Choose two)
- A. Classification
- B. Tagging
- C. Packet Scheduling
- D. Admission Control
- E. Resource Reservation
Answer: DE
NEW QUESTION 29
Which technology allows multiple instances of a routing table to coexist on the same router simultaneously?
- A. VRF
- B. Cisco virtual router
- C. Instanced virtuer router
- D. IS-IS
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 30
......
Thanks for reading the newest 300-320 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Simply pass 300-320 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.simply-pass.com/Cisco-exam/300-320-dumps.html (448 Q&As Dumps)