We provide real 642-885 exam questions and answers braindumps in two formats. Download PDF & Practice Tests. Pass Cisco 642-885 Exam quickly & easily. The 642-885 PDF type is available for reading and printing. You can print more and practice many times. With the help of our Cisco 642-885 dumps pdf and vce product and material, you can easily pass the 642-885 exam.
Cisco 642-885 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
A CRS router that runs Cisco IOS XR has dual routing processors installed. Which solution should be implemented to prevent OSPF adjacency flapping if the primary routing processor fails?
- A. NSR
- B. OSPF Fast Timers
- C. OSPF RE Sync
- D. router msdp
- E. NSF
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 2
Which two options are thecommon methods for implementing Site of Origin on Cisco IOS XE routers for loop avoidance in multihome BGP customers? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure the route-map in command on the CE BGP neighbor.
- B. Configure Site of Origin directly on the CE BGP neighbor command.
- C. Configure site-map on VRF interface and redistribution of iBGP.
- D. Configure site-map on VRF interface and network command.
- E. Configure the route-map out command on the P router.
Answer: AB
NEW QUESTION 3
With PIM-SM operations, which four pieces of information are maintained in the multicast routing table for each (*,G) or (S,G) entry? (Choose four.)
- A. RPF Neighbor
- B. RP Set
- C. Incoming Interface
- D. OIL
- E. DF priority
- F. PIM SM state flags
Answer: ACDF
Explanation:
The following is sample output from the show ip mroute command for a router operating in sparse mode:
show ip mroute
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, C - Connected, L - Local, P - Pruned R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set
Timers: Uptime/Expires
Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop, State/Mode
(*, 224.0.255.3), uptime 5:29:15, RP is 198.92.37.2, flags: SC
Incoming interface: Tunnel0, RPF neighbor 10.3.35.1, Dvmrp Outgoing interface list:
Ethernet0, Forward/Sparse, 5:29:15/0:02:57
(198.92.46.0/24, 224.0.255.3), uptime 5:29:15, expires 0:02:59, flags: C
Incoming interface: Tunnel0, RPF neighbor 10.3.35.1 Outgoing interface list:
Ethernet0, Forward/Sparse, 5:29:15/0:02:57
NEW QUESTION 4
What must occur before an (S,G) entry can be populated in the multicast routing table?
- A. The (*,G) entry must have timed out
- B. The (*,G) entry OIL must be null
- C. The router must be directly connected to the multicast source
- D. The parent (*,G) entry must be created first
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 5
A junior network engineer has just configured a new IBGP peering between two Cisco ASR9K PE routers in the network using the loopback interface of the router, but the IBGP neighborship is not able to be established. Which two verification steps will be helpful in troubleshooting this problem? (Choose two.)
- A. Verify that the network command under router BGP is configured correct on each router for announcing the router's loopback interface in BGP
- B. Verify that the ibgp-multihop command under the BGP neighbor is configured correctly on each router
- C. Verify that the loopback interfaces are reachable over the IGP
- D. Verify that the update-source loopback command under the BGP neighbor is configured correctly on each router
- E. Verify that the ttl-security command under the BGP neighbor is configured correctly on each router to enable the router to send the BGP packets using a proper TTL value
- F. Verify that the UDP port 179 traffic is not being blocked by an ACL or firewall between the two IBGP peers
Answer: CD
NEW QUESTION 6
What is one of the configuration errors within an AS that can stop a Cisco IOS-XR router from announcing certain prefixes to its EBGP peers?
- A. Some prefixes were mistagged with the no-export BGP community
- B. Some prefixes were set with an MED of 0
- C. The outbound BGP route policy only has set actions defined without any pass actions defined
- D. The inbound BGP route policy only has set actions defined without any pass actions defined
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
Which multicast routing protocol is used to forward multicast data along the optimal path from source to receivers?
- A. PIM DM
- B. PIM Bi-Dir
- C. PIM SM
- D. SSM
- E. IGMP
- F. MSDP
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 8
Which two statements correctly describe the RPF check when a multicast packet arrives at a router? (Choose two.)
- A. The router looks up the source address in the unicast routing table to determine if the packet has arrived on the interface that is on the reverse path back to the source
- B. The router looks up the destination address in the unicast routing table to determine if the packet has arrived on the interface that is on the reverse path back to the destination
- C. If the packet has arrived on the interface leading back to the destination, the RPF check passes and the packet is forwarde
- D. If the RPF check fails, the packet is dropped
- E. If the packet has arrived on the interface leading back to the source, the RPF check passes and the packet is forwarde
- F. If the RPF check fails, the packet is dropped
Answer: AD
Explanation:
Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF)
RPF is a fundamental concept in multicast routing that enables routers to correctly forward multicast traffic down the distribution tree. RPF makes use of the existing unicast routing table to determine the upstream and downstream neighbors. A router will only forward a multicast packet if it is received on the upstream interface.
This RPF check helps to guarantee that the distribution tree will be loop free. RPF Check
When a multicast packet arrives at a router, the router will perform an RPF check on the packet. If the RPF check is successful, the packet will be forwarded. Otherwise it will be dropped.
For traffic flowing down a source tree, the RPF check procedure works as follows:
Step 1. Router looks up the source address in the unicast routing table to determine if it has arrived on the interface that is on the reverse path back to the source.
Step 2. If packet has arrived on the interface leading back to the source, the RPF check is successful and the packet will be forwarded.
Step 3. If the RPF check in 2 fails, the packet is dropped.
NEW QUESTION 9
Refer to the Cisco IOS-XR BGP configuration exhibit.
Identify two configuration errors. (Choose two.)
- A. The neighbor-group efg is missing the ebgp-multihop 2 configuration
- B. The ttl-security configuration command is missing the option to set the number of hops
- C. The passall route policy is wrong
- D. The route-policy passall in and route-policy passall out commands should be configured under the neighbor-group efg instead of the af-group abc
- E. The maximum-prefix 10 configuration should be configured under the af-group abc instead of the neighbor-group efg
Answer: CE
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_configuration_example09186a00801 0a28a.shtml
NEW QUESTION 10
In Cisco IOS-XR, the maximum-prefix command, to control the number of prefixes that can be installed from a BGP neighbor, is configured under which configuration mode?
- A. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P2(config-bgp)#
- B. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P2(config-bgp-af)#
- C. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P2(config-bgp-nbr)#
- D. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P2(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_configuration_example09186a00801 0a28a.shtml
NEW QUESTION 11
Refer to the Cisco IOS-XR show output exhibit.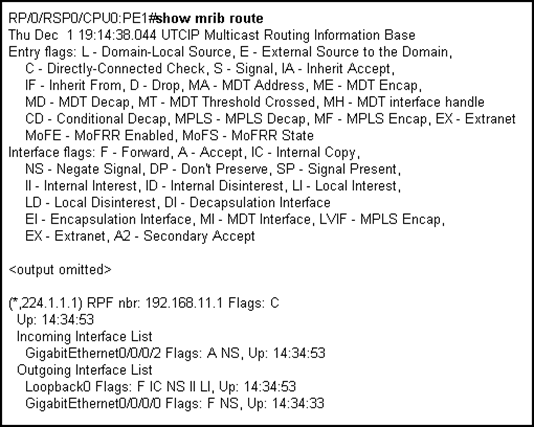
Which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. The RPF neighbor 192.168.11.1 is the path towards the RP for the 224.1.1.1 multicast group
- B. The RP for the 224.1.1.1 multicast group is reachable over the Gi0/0/0/0 interface
- C. This router is the RP for the 224.1.1.1 multicast group
- D. Incoming 224.1.1.1 multicast group traffic will be sent out through the Gi0/0/0/0 interface
- E. Incoming 224.1.1.1 multicast group traffic will be sent out through the Gi0/0/0/2 interface
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 12
When configuring PIM operations, what is the effect of setting the SPT threshold to infinity?
- A. The multicast source to the RP path will never switch over to the shortest path tree
- B. All the PIM routers will have more (S,G) states, thus consuming more router resources
- C. The receivers will be able to immediately switch over to the shortest path tree after receiving the first multicast packets on the shared tree via the RP
- D. The last-hop routers will never switch over to the shortest path tree and will always remain on the shared tree
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the Cisco IOS-XR show output exhibit.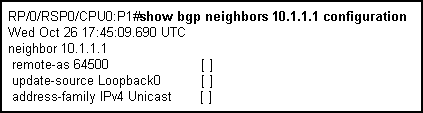
Which statement is correct?
- A. The [ ] indicates the configuration has a problem
- B. The [ ] indicates the 10.1.1.1 neighbor peering session has not been established
- C. The [ ] indicates the configuration was not inherited from a group
- D. The [ ] indicates the configuration has not been committed
- E. The [ ] indicates the corresponding BGP peer configuration has a mismatch configuration
Answer: C
Explanation:
show bgp neighbors
Use the show bgp neighbors command to display information about the BGP configuration for neighbors.
•Use the configuration option to display the effective configuration for the neighbor, including any settings that have been inherited from session groups, neighbor groups, or af-groups used by this neighbor.
•Use the inheritance option to display the session groups, neighbor groups, and af-groups from which this neighbor inherits configuration settings.
The following example displays sample output from the show bgp af-group command using the configuration keyword. This example shows where each configuration item was
inherited from. The default-originate command was configured directly on this address family group (indicated by [ ]). The remove-private-as command was inherited from address family group GROUP_2, which in turn inherited from address family group GROUP_3:
NEW QUESTION 14
An SP core is running PIM on the network. Multicast groups in this networkare in the 232.0.0.0/8 range. Which commandenables multicast routing operations without using an RP?
- A. ip pim autorp
- B. ip pim ssm default
- C. ip pim bidir-enable
- D. ip pim register-source
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two statements regarding Auto RP operations and implementations are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. Candidate RPs send RP announcements to the 224.0.1.39 multicast group, and the mapping agents send RP discovery messages to the 224.0.1.40 multicast group
- B. Every PIM-SM router must be configured with the RP mapping agent IP address
- C. Candidate RPs learn the IP address of the mapping agents via periodic RP discovery messages
- D. Administrative scoping can be configured to limit the scope of the RP announcements
- E. A Reverse Path Forwarding check is done on the RP discovery messages
- F. RP discovery messages are flooded hop by hop throughout the network as multicast to the all PIM routers multicast group with a TTL of 1
Answer: AD
Explanation:
Auto-RP
Automatic route processing (Auto-RP) is a feature that automates the distribution of group- to-RP mappings in a PIM network. This feature has these benefits:
It is easy to use multiple RPs within a network to serve different group ranges. It allows load splitting among different RPs.
It facilitates the arrangement of RPs according to the location of group participants.
It avoids inconsistent, manual RP configurations that might cause connectivity problems. Multiple RPs can be used to serve different group ranges or to serve as hot backups for each other. To ensure that Auto-RP functions, configure routers as candidate RPs so that they can announce their interest in operating as an RP for certain group ranges. Additionally, a router must be designated as an RP-mapping agent that receives the RP- announcement messages from the candidate RPs, and arbitrates conflicts. The RPmapping agent sends the consistent group-to-RP mappings to all remaining routers. Thus, all routers automatically determine which RP to use for the groups they support auto- rp candidate-rp
To configure a router as a Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) rendezvous point (RP) candidate that sends messages to the well-known CISCO-RP-ANNOUNCE multicast group
(224.0.1.39), use the auto-rp candidaterp command in PIM configuration mode. To return to the default behavior, use the no form of this command. auto-rp candidate-rp type interface-path-id scope ttl-value [ group-list access-listname ] [ interval seconds ] [bidir] no auto-rp candidate-rp type interface-path-id scope ttl-value [ group-list access-listname] [ interval seconds ] [bidir]
NEW QUESTION 16
Which informationdoes the multicast supported router need to forward the multicast traffic over the source or shared tree?
- A. source address
- B. multicast address
- C. destination address
- D. mGRE headers
- E. MDT Data
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 17
Which two functions are supported for BGP extension MP-BGP for IP multicasting? (Choose two.)
- A. A network can support incongruent unicast and multicast topologies.
- B. A network can support congruent unicast and multicast topologies.
- C. MP-BGP is an enhanced BGP that carries routing information for multiple network layer protocols and IP multicast routes.
- D. MP-BGP carries single sets of routes for unicast routing and multicast routing.
- E. MP-BGP is useful when a link dedicated to multicast and unicast traffic is desired.
Answer: AC
NEW QUESTION 18
Which multicast routing protocol is most optimal for supporting many-to-many multicast applications?
- A. PIM-SM
- B. PIM-BIDIR
- C. MP-BGP
- D. DVMRP
- E. MSDP
Answer: B
Explanation:
PIM-Bidirectional Operations
PIM Bidirectional (BIDIR) has one shared tree from sources to RP and from RP to receivers. This is unlike the PIM-SM, which is unidirectional by nature with multiple source trees - one per (S, G) or a shared tree from receiver to RP and multiple SG trees from RP to sources.
Benefits of PIM BIDIR are as follows:
• As many sources for the same group use one and only state (*, G), only minimal states are required in each router.
• No data triggered events.
• Rendezvous Point (RP) router not required. The RP address only needs to be a routable address and need not exist on a physical device.
NEW QUESTION 19
A network engineer of an ISP using Cisco IOS XR routers wants to limit the number of prefixes that BGP peers can accept. To accomplish this task, the command maximum- prefix 1000 is used. Which two results of this configuration are expected? (Choose two.)
- A. A warning message displays by default when 750 prefixes are received.
- B. A warning message displays by default when 850 prefixes are received.
- C. A BGP peer resets when it receives 1001 prefixes.
- D. A BGP peer resets when it receives 1000 prefixes.
- E. A BGP peer ceases when it receives 1001 prefixes.
- F. A BGP peer ceases when it receives 1000 prefixes.
- G. The BGP peer tries to reestablish the session after one minute.
Answer: AE
NEW QUESTION 20
Which mechanism is used by an IPv6 multicast receiver to join an IPv6 multicast group?
- A. IGMP report
- B. IGMP join
- C. MLD report
- D. General query
- E. PIM join
Answer: C
Explanation:
MLD Reports
The processing of MLDv1 join messages is essentially the same as with IGMPv2. When no IPv6 multicast
routers are detected in a VLAN, reports are not processed or forwarded from the switch.
When IPv6 multicast
routers are detected and an MLDv1 report is received, an IPv6 multicast group address and an IPv6 multicast
MAC address are entered in the VLAN MLD database. Then all IPv6 multicast traffic to the group within the VLAN is forwarded using this address. When MLD snooping is disabled, reports are flooded in the ingress VLAN.
When MLD snooping is enabled, MLD report suppression, called listener message suppression, is automatically enabled. With report suppression, the switch forwards the first MLDv1 report received by a group to IPv6 multicast routers; subsequent reports for the group are not sent to the routers. When MLD snooping is disabled, report suppression is disabled, and all MLDv1 reports are flooded to the ingress VLAN.
The switch also supports MLDv1 proxy reporting. When an MLDv1 MASQ is received, the switch responds with MLDv1 reports for the address on which the query arrived if the group exists in the switch on another port and if the port on which the query arrived is not the last member port for the address.
NEW QUESTION 21
Refer to the configuration exhibit, taken from a Cisco IOS-XR router.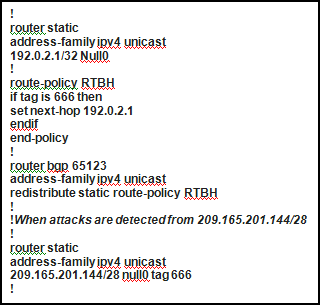
Which configuration change is required to properly enable this router as the signaling router for implementing source-based RTBH filtering?
- A. Set community (no-export) in the route policy
- B. Pass in the route policy
- C. Set local-preference 1000 in the route policy
- D. The 192.0.2.1/32 static route should be tagged as 666 (tag 666)
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 22
A network engineer must deploy an iBGP-based cloud region configuration by means of templates to reduce the overall BGP CLI required. Which three commands represent a basic configuration for a BGP peer session template on a regular Cisco IOS instance? (Choose three.)
- A. template peer-session session-template-name
- B. remote-as as-number
- C. neighbor-family config template
- D. peer-family config template
- E. as-override
- F. timers keepalive-interval hold-time
Answer: ABF
NEW QUESTION 23
Refer to the exhibit.
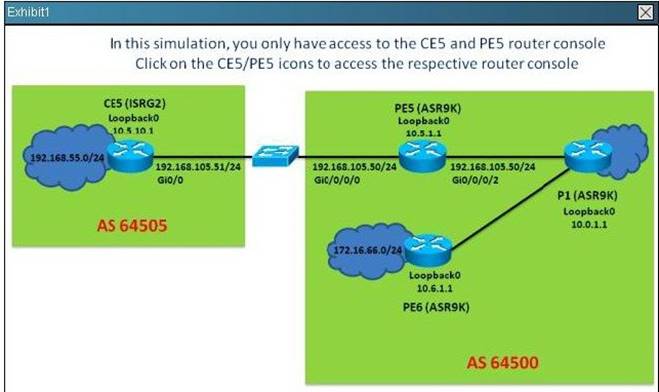
On the PE5 router, which statementis correct regarding the learned BGP prefixes?
- A. The 209.165.201.0/27 prefix is received from the 10.0.1.1 IBGP peer which is a route reflector
- B. The 172.16.66.0/24 prefix BGP next-hop points to the route reflector
- C. All prefixes learned on PE5 has the default local preference value
- D. The 209.165.202.128/27 prefix is originated by the 10.0.1.1 IBGP peer
Answer: C
Explanation:
#show ip bgp -- check i tag for PE5
NEW QUESTION 24
Which two actions result when a network administrator attempts to ping an IPv6 host on the LAN? (Choose two.)
- A. ARP is used to determine the MAC address of the destination host.
- B. Neighbor Discovery is used to determine the MAC address of the destination host.
- C. Neighbor Solicitation messages are sent out by the source host to determine the data link-layer address of the destination host.
- D. Neighbor Advertisement messages are sent by the source host to announce its presence on the local link.
- E. Router Solicitation messages are sent out on a specific multicast address to request the data link-layer address of the target device.
- F. Router Solicitation messages are sent to the local router on the network segment to request data link-layer information about the destination host.
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 25
Refer to the exhibit.
Which configuration is missing to complete the configuration task of enabling BFD with the 192.168.1.1 EBGP peer?
- A. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled globally under router bgp 64500 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp)#bfd fast-detect
- B. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled for the address-family under address-family ipv4 unicastRP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp-af)#bfd fast-detect
- C. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled for the 192.168.1.1 neighbor under neighbor 192.168.1.1RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp-nbr)#bfd fast-detect
- D. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled for the 192.168.1.1 neighbor address-family under neighbor 192.168.1.1 address-family ipv4 unicastRP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config-bgp-nbr-af)#bfd fast-detect
- E. bfd fast-detect also needs to be enabled globally on the router RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:P1(config)#bfd fast-detect
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 26
......
Recommend!! Get the Full 642-885 dumps in VCE and PDF From DumpSolutions, Welcome to Download: https://www.dumpsolutions.com/642-885-dumps/ (New 131 Q&As Version)