Proper study guides for Update Oracle Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator certified begins with Oracle 1Z0-821 preparation products which designed to deliver the Guaranteed 1Z0-821 questions by making you pass the 1Z0-821 test at your first time. Try the free 1Z0-821 demo right now.
Also have 1Z0-821 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which two options accurately describe the network characteristics of a zone?
- A. DHCP address assignment cannot be configured in a shared IP zone.
- B. Shared IP is the default type of network configuration.
- C. Exclusive IP is the default type of network configuration.
- D. By default, all IP addresses, netmasks, and routes are set by the global zone and cannot be altered in a non global zone.
- E. IPMP cannot be managed within the non-global zone.
- F. Commands such as snoop and dladm cannot be used on datalinks that are in use by a running zone.
Answer: AB
Explanation:
A: Non-global zones can not utilize DHCP (neither client nor server).
B (not C): By default, non-global zones will be configured with a shared IP functionality. What this means is that IP layer configuration and state is shared between the zone you’re creating and the global zone. This usually implies both zones being on the same IP subnet for each given NIC.
Note: A zone is a virtual operating system abstraction that provides a protected environment in which applications run. The applications are protected from each other to provide software fault isolation. To ease the labor of managing multiple applications and their environments, they co-exist within one operating system instance, and are usually managed as one entity.
The original operating environment, before any zones are created, is also called the "global zone" to distinguish it from non-global zones, The global zone is the operating system instance.
Incorrect Answer
E: Exclusive-IP zones can use IPMP. IPMP is configured the same way in an exclusive-IP zone as it is on a system not using zones.
For shared-IP zones, IPMP can be configured in the global zone. F: Full IP-level functionality is available in an exclusive-IP zone. An exclusive-IP zone has its own IP-related state.
An exclusive-IP zone is assigned its own set of data-links using the zonecfg command. The zone is given a data-link name such as xge0, e1000g1, or bge32001, using the physical property of the net resource. The address property of the net resource is not set.
Note that the assigned data-link enables the snoop command to be used.
The dladm command can be used with the show-linkprop subcommand to show the assignment of data-links to running exclusive-IP zones.
NEW QUESTION 2
Review the storage pool information: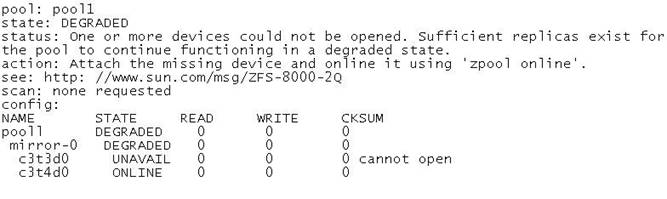
Choose the correct procedure to repair this storage pool.
- A. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- B. When the system is booted, execute the zpool clear pool1 command.
- C. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- D. When the system is booted execute the zpool online pool1 command.
- E. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- F. When the system is booted, execute the zpool replace pool1 c3t3d0 command.
- G. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- H. When the system is booted, execute the zpool replace pool1 c3t3d0 c3t3d0 command.
Answer: C
Explanation:
You might need to replace a disk in the root pool for the following reasons: The root pool is too small and you want to replace it with a larger disk
The root pool disk is failing. In a non-redundant pool, if the disk is failing so that the system won't boot, you'll need to boot from an alternate media, such as a CD or the network, before you replace the root pool disk.
In a mirrored root pool configuration, you might be able to attempt a disk replacement without having to boot from alternate media. You can replace a failed disk by using the zpool replace command.
Some hardware requires that you offline and unconfigure a disk before attempting the zpool replace operation to replace a failed disk.
For example:
# zpool offline rpool c1t0d0s0
# cfgadm -c unconfigure c1::dsk/c1t0d0
<Physically remove failed disk c1t0d0>
<Physically insert replacement disk c1t0d0>
# cfgadm -c configure c1::dsk/c1t0d0
# zpool replace rpool c1t0d0s0
# zpool online rpool c1t0d0s0
# zpool status rpool
<Let disk resilver before installing the boot blocks>
SPARC# installboot -F zfs /usr/platform/`uname -i`/lib/fs/zfs/bootblk /dev/rdsk/c1t0d0s0 x86# installgrub /boot/grub/stage1 /boot/grub/stage2 /dev/rdsk/c1t9d0s0
NEW QUESTION 3
Which two are implemented using the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)?
- A. ping
- B. DHCP
- C. HTTP
- D. telnet
- E. syslog
- F. traceroute
Answer: AF
Explanation:
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite.
ICMP differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications (with the exception of some diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute).
NEW QUESTION 4
Review the non-global zone configuration displayed below: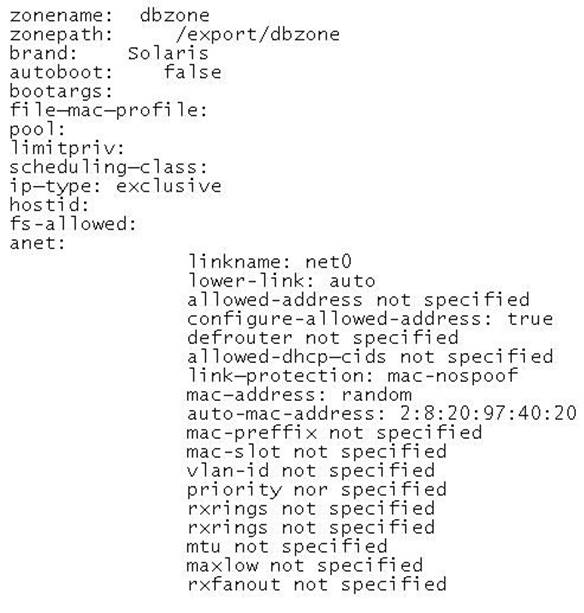
The global zone has 1024 MB of physical memory. You need to limit the non-global zone so that it uses no more than 500 MB of the global zone's physical memory. Which option would you choose?
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
- E. Option E
Answer: C
Explanation:
Add a memory cap.
zonecfg:my-zone> add capped-memory
Set the memory cap.
zonecfg:my-zone:capped-memory> set physical=50m End the memory cap specification.
zonecfg:my-zone:capped-memory> end
NEW QUESTION 5
The interface net3 should be operating, but is not. Command:
Which command should you enter next?
- A. ipadm create-ip
- B. ipadm enable-if
- C. ipadm show-if
- D. ipadm up-addr
Answer: B
Explanation:
Enable-if -t interface
Enables the given interface by reading the configuration from the persistent store. All the persistent interface properties, if any, are applied and all the persistent addresses, if any, on the given interface will be enabled.
-t, --temporary
Specifies that the enable is temporary and changes apply only to the active configuration.
NEW QUESTION 6
You enter dladm show-phys, which provides the following output:
You then enter: ipadm create-ip net3
What is the output?
- A. ipadm: cannot; create interface net3: Operation failed.
- B. ipadm: cannot create interface net3: Interface already exists.
- C. ipadm: cannot create interface net3: IP address object not specified.
- D. No_response, The command was successful.
Answer: B
Explanation:
According to the exhibit the interface already exists.
The command ipadm create-ip net3 is supposed to create a new interface net3.
NEW QUESTION 7
The global zone has 8 CPUS. YOU suspect that one of your non global /ones, dbzone, is consuming all of the CPU resources.
Which command would you use to view the CPU utilization for all of the zones to confirm this?
- A. Run from the global zone:prstat -Z
- B. Run from each zonezlogin <zonename> mpstat
- C. Run from the global zone:zonestar -r summary
- D. Run from the global zone:rctladm -1
- E. Run from the global zone:prctl -i
Answer: A
Explanation:
If you're logged on to the system, you can run prstat -Z to generate a summary of cpu/memory utilization by zone.
NEW QUESTION 8
You are the administrator of a system that a large number of developers work on. These developers crash the system, and their applications, on a regular basis.
What command would you use to configure where the core files are saved?
- A. savecore
- B. dumpadm
- C. svcadm
- D. proc
- E. coreadm
Answer: E
Explanation:
The coreadm command is used to specify the name and location of core files produced by abnormally-terminating processes.
NEW QUESTION 9
Which modification needs to be made to the Service Management Facility before you publish a new package to the IPS repository?
- A. The pkg.depotd must be disabled.
- B. The pkg/readonly property for the application/pkg/server service must be set to false.
- C. The Pkg/writabie_root property for the application/Pkg/server service must be set to true.
- D. The pkg/image.root property for the application/pkg/server service must be set to the location of the repository.
Answer: D
Explanation:
pkg/image_root
(astring) The path to the image whose file information will be used as a cache for file data.
NEW QUESTION 10
View the Exhibit and review the file system information displayed from a remote server.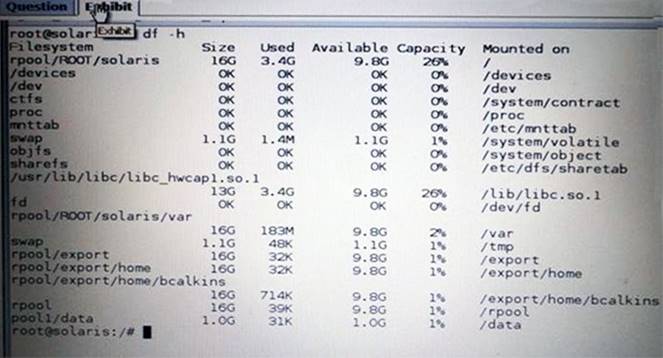
You are configuring a new server. This new server has the following storage pool configured:
This new server also has the following file systems configured: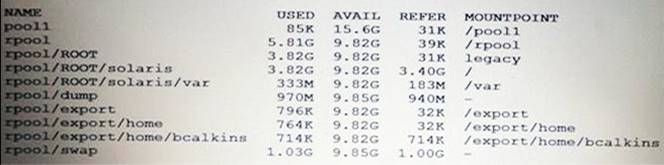
When you are finished building this new server, the pool1/data dataset must be an exact duplicate of note server. What is the correct procedure to create the pool1/data dataset on this new server?
- A. zfs create –o mountpoint=/data –o refquota=1g pool1/data
- B. zfs set mountpoint=none pool1zfs create pool1/data
- C. zfs set mountpoint=none pool1zfs create –o mountpoint=/data –o quota=1g pool1/data
- D. zfs create quota=1g pool1/data
- E. zfs create mountpoint=/data pool1/data
- F. zfs set quota=1g pool1/data
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 11
Your SPARC server will not boot into multi user-server milestones and you need to troubleshoot to out why. You need to start the server with minimal services running so that you can go through each milestone manually to troubleshoot the issue.
Select the option that boots the server with the fewest services running.
- A. boot -s
- B. boot milestone none
- C. boot -m milestone=single-user
- D. boot -m milestone=none
- E. boot -m none
Answer: D
Explanation:
The command boot -m milestone=none is useful in repairing a system that have problems booting early.
Boot Troubleshooting:
To step through the SMF portion of the boot process, start with: boot -m milestone=none
Then step through the milestones for the different boot levels: svcadm milestone svc:/milestone/single-user:default
svcadm milestone svc:/milestone/multi-user:default svcadm milestone svc:/milestone/multi-user-server:default
NEW QUESTION 12
Which operation will fail if the DNS configuration is incorrect?
- A. domainname
- B. ping localhost.
- C. ping 192.168.1.1
- D. ping 23.45.82.174
- E. ping www.oracle.com.
- F. cat /etc/resolv.conf
Answer: E
Explanation:
www.oracle.com would have to be resolved to an IP name by the domain name service.
NEW QUESTION 13
Which files must be edited in order to set up logging of all failed login attempts?
- A. /etc/default/login, /var/adm/loginlog, /etc/syslog.conf
- B. /etc/default/login, /var/adm/authlog, /etc/syslog.conf
- C. /var/adm/loginlog, /var/adm/authlog, /etc/syslog.conf
- D. /etc/default/login, /var/adm/authlog, /var/adm/loginlog
Answer: B
Explanation:
This procedure captures in a syslog file all failed login attempts.
1. Set up the /etc/default/login file with the desired values for SYSLOG and SYSLOG_FAILED_LOGINS
Edit the /etc/default/login file to change the entry. Make sure that SYSLOG=YES is uncommented.
2. Create a file with the correct permissions to hold the logging information. Create the authlog file in the /var/adm directory.
3. Edit the syslog.conf file to log failed password attempts. Send the failures to the authlog file.
NEW QUESTION 14
A local repository is available on this system and you need to enable clients to access this repository via HTTP. The repository information is:
PUBLISHERTYPESTATUSURI
solarisoriginonlinehttp://sysA.example.com
Identify two of the steps that are required to make the local repository on this server available to the client via HTTP.
- A. On the server: set the pkg/inst_root and pkg/readonly properties for the svc:/application/pkg/server:default service and enabled the service
- B. On the server: set the sharefs property on the ZFS file system containing the IPS repository.
- C. On the client: reset the origin for the solaris publisher.
- D. On the client: set the pkg/inst_root and pkg/readonly properties for the svc:/application/server:default service enable the service.
- E. On the client: start the pkg.depotd process.
Answer: AE
Explanation:
A: Configure the Repository Server Service
To enable clients to access the local repository via HTTP, enable the application/pkg/server Service Management Facility (SMF) service.
# svccfg -s application/pkg/server setprop pkg/inst_root=/export/repoSolaris11
# svccfg -s application/pkg/server setprop pkg/readonly=true
E: Use pkg.depotd to serve the repository to clients. Start the Repository Service
Restart the pkg.depotd repository service.
# svcadm refresh application/pkg/server
# svcadm enable application/pkg/server
To check whether the repository server is working, open a browser window on the localhost location.
NEW QUESTION 15
The line
set noexec_user_stack= l
should be added to the /etc/system file to prevent an executable stack while executing user programs. What is the purpose of this?
- A. help prevent core dumps on program errors
- B. help programs to execute more quickly by keeping to their own memory space
- C. log any messages into the stack log
- D. help make buffer-overflow attacks more difficult
Answer: D
Explanation:
How to Disable Programs From Using Executable Stacks Purpose: Prevent executable stack from overflowing. You must be in the root role.
Edit the /etc/system file, and add the following line: set noexec_user_stack=1
Reboot the system.
# reboot
NEW QUESTION 16
A user account must be a member of a primary group, and may also be a member of one or more secondary groups. What is the maximum total number of groups that one user can concurrently belong to?
- A. 15
- B. 16
- C. 17
- D. 63
- E. 64
- F. 65
- G. The number of groups one user can concurrently belong to is unlimited in Solaris 11.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Each user belongs to a group that is referred to as the user’s primary group. The GID number, located in the user’s account entry within the /etc/passwd file, specifies the user’s primary group.
Each user can also belong to up to 15 additional groups, known as secondary groups. In the /etc/group file, you can add users to group entries, thus establishing the user’s secondary group affiliations.
Note (4 PSARC/2009/542):
his project proposes changing the maximum value for NGROUPS_MAX from 32 to 1024 by changing the definition of NGROUPS_UMAX from 32 to 1024.
The use for a larger number of groups is described in CR 4088757, particular in the case of Samba servers and ADS clients; the Samba servers map every SID to a Unix group. Users with more than 32 groups SIDs are common. We've seen reports varying from "64 is enough", "128 is absolutely enough" and "we've users with more 190 group SIDS).
NGROUPS_MAX as defined by different Unix versions are as follows (http://www.j3e.de/ngroups.html):
Linux Kernel >= 2.6.3 65536
Linux Kernel < 2.6.3 32 Tru64 / OSF/1 32
IBM AIX 5.2 64
IBM AIX 5.3 ... 6.1 128
OpenBSD, NetBSD, FreeBSD, Darwin (Mac OS X) 16 Sun Solaris 7, 8, 9, 10 16 (can vary from 0-32)
HP-UX 20
IRIX 16 (can vary from 0-32)
Plan 9 from Bell Labs 32
Minix 3 0 (Minix-vmd: 16)
QNX 6.4 8
NEW QUESTION 17
You need to know the IP address configured on interface net3, and that the interface is up. Which command confirms these?
- A. ipadm show-if
- B. ipadm up-addr
- C. ipadm show-addr
- D. ipadm enable-if
- E. ipadm refresh-addr
- F. ipadm show-addrprop
Answer: C
Explanation:
Show address information, either for the given addrobj or all the address objects configured on the specified interface, including the address objects that are only in the persistent configuration.
State can be: disabled, down, duplicate, inaccessible, ok, tentative Example:
# ipadm show-addr
ADDROBJ TYPE STATE ADDR
lo0/v4 static ok 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok ::1/128
NEW QUESTION 18
The ZFS configuration on your server is:
Pool1 6.67G31K/pool Pool1/data31K31K/data
Select the three commands that you would use to 1. Create, 2. List, and 3. Delete a snapshot of the /data file system.
- A. zfs snapshot pool1/data@now
- B. zfs create snapshot pool1/data@now
- C. zfs list -t snapshot
- D. zfs list -t snapshot pool1/data
- E. zfs destroy pool1/data@now
- F. zfs destroy snapshot pool1/data@now
Answer: ADE
Explanation:
A: Snapshots are created by using the zfs snapshot command, which takes as its only argument the name of the snapshot to create.
D: You can list snapshots as follows:
# zfs list -t snapshot
E: Snapshots are destroyed by using the zfs destroy command. For example:
# zfs destroy tank/home/ahrens@now
NEW QUESTION 19
You have been asked to terminate a process that appears to be hung and will not terminate. The process table is shown below:
root 15163 15156 0 12:51:15 pts/3 0:00 hungscript What command will terminate the process?
- A. kill -9 15163
- B. kill -1 15163
- C. kill -15 15163
- D. kill -2 15163
Answer: A
Explanation:
Here we should use SIGTERM to terminate the process. Note:
When no signal is included in the kill command-line syntax, the default signal that is used is
–15 (SIGKILL). Using the –9 signal (SIGTERM) with the kill command ensures that the process terminates promptly. However, the –9 signal should not be used to kill certain processes, such as a database process, or an LDAP server process. The result is that data might be lost.
Tip - When using the kill command to stop a process, first try using the command by itself, without including a signal option. Wait a few minutes to see if the process terminates before
using the kill command with the -9 signal.
NEW QUESTION 20
Which network protocol is responsible for routing packets from one network to another?
- A. TCP
- B. UDP
- C. IP
- D. ICMP
- E. Ethernet
Answer: C
Explanation:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
NEW QUESTION 21
View the Exhibit to inspect the boot environment Information displayed within a non global zone on your system.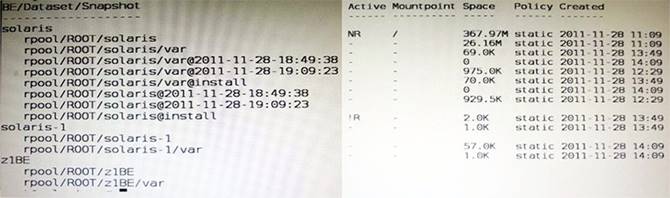
Which two options describe the solaris-1 boot environment?
- A. The solaris-1 boot environment is not bootable.
- B. The solaris-1 boot environment is incomplete.
- C. The solaris-1 boot environment was created automatically when the non global zone was created.
- D. The solaris-1 boot environment was created in the non-global zone using the beadm create command.
- E. The solaris-1 boot environment is associated with a non active global zone boot environment.
Answer: AE
Explanation:
A: The – of the Active Column indicates that this boot environment is inactive, and hence not bootable.
Note: The values for the Active column are as follows: R – Active on reboot.
N – Active now.
NR – Active now and active on reboot. “-” – Inactive.
“!” – Unbootable boot environments in a non-global zone are represented by an exclamation point.
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/html/E21801/unbootable.html#scrolltoc
NEW QUESTION 22
User brian changes the permissions for db_data this command: chmod 4755 db_data
What is true?
- A. db_data now has permissions rwsr-xr-x and can be deleted only by user brian.
- B. db_data now has permissions rwsr-xr-x and, if executed, will inn with the permissions of user brian.
- C. db_data now has permissions rwxr-sr-x and can be deleted only by members of the group owning it.
- D. The permissions for db_data cannot be determined, because the permissions prior to the change have not been specified.
- E. db_data must be an ordinary file, because special permissions cannot be set on a directory.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Use the chmod command to change permissions for a file or directory. You must be the owner of a file or directory, or have root access, to change its permissions.
Here we do not know if brian owns db_data. Note:
Permission 7 full
6 read and write
5 read and execute 4 read only
3 write and execute 2 write only
1 execute only
0 none
0 --- no permission 1 --x execute
2 -w- write
3 -wx write and execute 4 r-- read
5 r-x read and execute 6 rw- read and write
7 rwx read, write and execut
Solaris: Solaris Advanced User's Guide
NEW QUESTION 23
A user jack, using a bash shell, requests a directory listing as follows: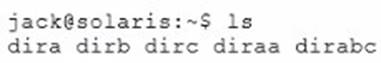
Which three statements are correct?
- A. The pattern dir? will expand to dira dirb dirc.
- B. The pattern dir*a will expand to diraa.
- C. The pattern dir*a will expand to dira diraa.
- D. The pattern dir*b? will expand to dirabc.
- E. The pattern dir*b? will expand to dirb dirabc.
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
A: dir followed by a single letter.
C: dir followed by any characters ending with a.
D: dir followed by any characters, then character b, then one single character. only dirabc matches
NEW QUESTION 24
......
P.S. Certleader now are offering 100% pass ensure 1Z0-821 dumps! All 1Z0-821 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.certleader.com/1Z0-821-dumps.html (243 New Questions)