we provide Certified Oracle 1Z0-821 braindumps which are the best for clearing 1Z0-821 test, and to get certified by Oracle Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator. The 1Z0-821 Questions & Answers covers all the knowledge points of the real 1Z0-821 exam. Crack your Oracle 1Z0-821 Exam with latest dumps, guaranteed!
Free 1Z0-821 Demo Online For Oracle Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
Consider the following commands: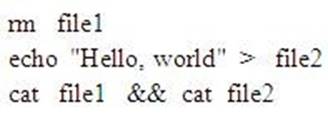
What is displayed when this sequence of commands is executed using the bash shell?
- A. Hello, world
- B. cat: cannot open file1
- C. cat: cannot open file1Hello, world
- D. cat: cannot open file1 Hello, World
- E. bash: syntax error near unexpected token '&&'
Answer: B
Explanation:
First line (rm file1) deletes/removes file1. Second line captures the text into file2.
The first part of line 3 (cat file1) fails as the file1 does not exist.
The && (AND) operator will ensure that the third line fails. The result of line 3 will be the result of first part of line 3 (cat file1).
Note: cat - concatenate files and print on the standard output
Note #1: A list is a sequence of one or more pipelines separated by one of the operators ‘;’, ‘&’, ‘&&’, or ‘||’, and optionally terminated by one of ‘;’, ‘&’, or a newline.
Of these list operators, ‘&&’ and ‘||’ have equal precedence, followed by ‘;’ and ‘&’, which have equal precedence.
AND and OR lists are sequences of one or more pipelines separated by the control operators ‘&&’ and ‘||’, respectively. AND and OR lists are executed with left associativity.
An AND list has the form command1 && command2
command2 is executed if, and only if, command1 returns an exit status of zero.
An OR list has the form command1 || command2
command2 is executed if, and only if, command1 returns a non-zero exit status.
The return status of AND and OR lists is the exit status of the last command executed in the list.
Note #2 (on exit status): Zero means command executed successfully, if exit status returns non-zero value then your command failed to execute.
NEW QUESTION 2
You want to delete the IPv4 address on the interface net3. Which command should you use?
- A. ipadm delete-ip net3/v4
- B. ipadm down-addr net3/v4
- C. ipadm disable-if net3/v4
- D. ipadm delete-vni net3/v4
- E. ipadm delete-addr net3/v4
- F. ipadm deiete-ipv4 ner3/v4
Answer: E
Explanation:
The ipadm delete-addr subcommand removes addresses from interfaces. To remove an address from the IPMP group, type the following command:
# ipadm delete-addr addrobj
The addrobj uses the naming convention inder-interface/user-string.
NEW QUESTION 3
Identify three differences between the shutdown and init commands.
- A. Only shutdown broadcasts a final shutdown warning to all logged-in users.
- B. init does not terminate all services normall
- C. The shutdown command performs a cleaner shutdown of all services.
- D. The shutdown command can only bring the system to the single-user mileston
- E. The init command must be used to shut the system down to run level 0.
- F. Only shutdown sends a shutdown message to any systems that are mounting resources from the system that is being shut down.
- G. The shutdown command will shut the system down and turn off power; init will only shut the system down.
Answer: ABE
NEW QUESTION 4
You have been asked to troubleshoot the initial configuration of a virtual network connecting two local zones with the outside world.
View the exhibit.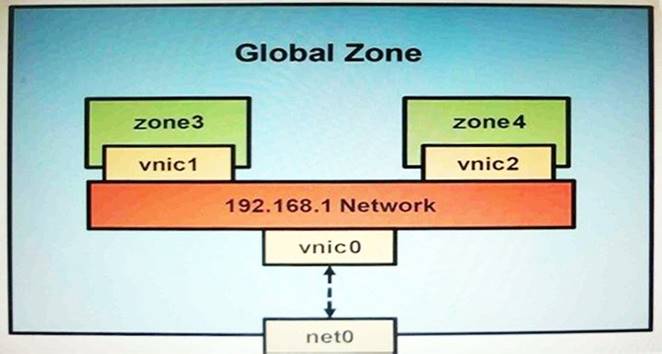
The command
dladm create-vnic -1 vswitch192.168.1 vnic1 fails with the error
dladm: invalid link name ‘vswitch192.168.1’ What is the reason for this error?
- A. The name vswitch192.168.1 is not legal.
- B. The zone must be specified withdladm create-vnic -z zone3 vnic1.
- C. The virtual interface must be specified withdladm create-vnic -z zone3 vnic1.
- D. The virtual interface must be created withipadm create-vnic -1 switch192.168.1.
- E. The virtual switch must be created first withdladm create -etherstub vswitch192.168.1.
Answer: E
Explanation:
There is no data-link named vswitch192.168. We need to create an etherstub first.
See Note and example below for details.
Note: Create a VNIC in the system's global zone.
# dladm create-vnic -l data-link vnic-name
data-link is the name of the interface where the VNIC is to be configured.
-l link, --link=link
link can be a physical link or an etherstub.
vnic-name is the name that you want to give the VNIC.
For example, to create a VNIC named vnic0 on interface e1000g0, you would type the following:
# dladm create-vnic -l e1000g0 vnic0
Example: Creating a Virtual Network Without a Physical NIC First, create an etherstub with name stub1:
# dladm create-etherstub stub1
Create two VNICs with names hello0 and test1 on the etherstub. This operation implicitly creates a virtual switch connecting hello0 and test1.
# dladm create-vnic -l stub1 hello0
# dladm create-vnic -l stub1 test1
NEW QUESTION 5
In an effort to reduce storage space on your server, you would like to eliminate duplicate copies of data in your server’s ZFS file systems.
How do you specify that pool1/data should not contain duplicate data blocks (redundant data) on write operations?
- A. zfs create - o compression=on pool1/data
- B. zpool create -o deduplication =on pool1; zfs create pool1/data
- C. zfs create - o deduplication=on pool1; zfs create pool1/data
- D. zfs create - o dedupratio=2 pool1/data
- E. zfs create - o dedup=on pool1/data
Answer: E
Explanation:
ZFS Deduplication Property
Solaris Express Community Edition, build 129: In this Solaris release, you can use the deduplication property to remove redundant data from your ZFS file systems. If a file system has the dedup property enabled, duplicate data blocks are removed synchronously. The result is that only unique data is stored and common components are shared between files.
You can enable this property as follows:
# zfs set dedup=on tank/home
NEW QUESTION 6
You suspect a problem with the oponldap package and want to make sure that the files have not be modified or otherwise tampered with.
Which command would validate all of the files contained in the openldap package and report any problems?
- A. pkgchk openldap
- B. pkginfo openldap
- C. pkg contents openldap
- D. pkg verify openldap
- E. pkg set-property signature-policy verify
Answer: A
Explanation:
pkgchk checks the accuracy of installed files or, by using the -l option, displays information about package files. pkgchk checks the integrity of directory structures and files. Discrepancies are written to standard error along with a detailed explanation of the problem.
NEW QUESTION 7
When speaking to an Oracle Support Engineer, you are asked to verify the version of the Solaris 11 build currently running on your system.
Which command would display the Solaris 11 build version currently running on your system?
- A. pkg info all
- B. cat /etc/release
- C. cat /etc/update
- D. prtconf | grep –i update
- E. pkg info entire
Answer: B
Explanation:
Which Solaris release you are running on your system can be determined using the following command:
cat /etc/release
This will tell you which release you are running and when it was released. The more recent your system, the more info is contained in this file.
Example:
# cat /etc/release
Oracle Solaris 10 8/11 s10s_u10wos_17b SPARC
Copyright (c) 1983, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Assembled 23 August 2011
NEW QUESTION 8
You are troubleshooting a newly installed desktop Oracle Solaris 11 system with a single network interface. From this system, you can connect to other systems within the company
intranet, but cannot access any external services (such as websites and email), even when using IP addresses.
Examining the routing table confirms that the default route to 192.168.1.1 is missing. DHCP is not used at this site. Which two commands will temporarily mid permanently configure the default route?
- A. ipadm set-gateway 192.168.1.1
- B. route add default 192.168.1.1
- C. ipadm set-default 192.168.1.1
- D. dladm route-add –d 192.168.1.1
- E. echo 192.168.1.1 >/etc/gateway
- F. echo 192.168.1.1 >/etc/defaultrouter
Answer: BF
Explanation:
B: Setting the default route on Solaris is easy. If you are trying to just set the route temporarily you can use the route command:
Route add default <ipaddress> Example:
Route add default 192.168.1.1
Note: Route command manipulates the kernel routing tables. Routing is the process of forwarding a packet from one computer to another. It is based on the IP address in the IP packet header and netmask.
F: If you want the route to be persisted when you reboot the system, you will need to set the route in the /etc/defaultrouter file.
/etc/defaultrouter Example:
Echo 192.168.1.1 > /etc/defaultrouter
NEW QUESTION 9
You need to migrate a UFS file system named /production_ufs to a ZFS file system named
/production_ufs. The /production_ufs file system cannot be taken down or be out of production during the migration, and the current /production_ufs file system must remain active until the /ptoduction_zfs file system is copied and ready.
Which method allows you to meet both requirements?
1. Copy live data from /production_ufs to /production_zfs while /production_ufs is in use.
2. When the copy is complete, /production_zfs will contain an up-to date copy of
/production_ufs
- A. Create a snapshot of the UFS file syste
- B. Create the new ZFS file syste
- C. Use cpio to copy data from the snapshot to the new ZFS file system.
- D. Create a new Boot Environmen
- E. Create the ZFS file syste
- F. Use lucreate -m to copy data from the Current UFS file system to the new ZFS file system.
- G. Mirror the existing UFS file system by using SVM.After both submissions are in sync, migrate one of the submissions to a ZFS file System by using Live Upgrade.
- H. Create the new ZFS file system by using zfs create import to import data from the existing UFS file system into the new ZFS file system
- I. Create the new zfs file system by using the zfs create -o shadow.
Answer: E
Explanation:
Migrating Data With ZFS Shadow Migration
ZFS shadow migration is a tool you can use to migrate data from an existing file system to a new file system. A shadow file system is created that pulls data from the original source as necessary.
You can use the shadow migration feature to migrate file systems as follows:
* A local or remote ZFS file system to a target ZFS file system
* A local or remote UFS file system to a target ZFS file system
Shadow migration is a process that pulls the data to be migrated:
* Create an empty ZFS file system.
* Set the shadow property on an empty ZFS file system, which is the target (or shadow) file system, to point to the file system to be migrated.
For example:
# zfs create -o shadow=nfs://system/export/home/ufsdata users/home/shadow2
* Data from file system to be migrated is copied over to the shadow file system.
NEW QUESTION 10
User jack, whose account is configured to use the korn shell, logs in and examines the value of his PATH environment variable:
What will happen, and why?
- A. He will get a "file not found" error, because the current directory is not in his seaech path.
- B. He will get a "file not found" error, because his home directory is not in his search path.
- C. The useradd script will execute, because jack is in the same directory that the script is located in.
- D. The command /user/sbin/useradd will execute, because it is the last match in the search path.
- E. The command /user/sbin/useradd will execute, because it is the first match in the search path.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 11
You display the IP interface information with ipmpstat -i.
Which two characteristics are indicated by characters that may be included in the FLAGS column?
- A. default route
- B. IP forwarding enabled IS
- C. allocated to global zone
- D. unusable due to being inactive
- E. nominated to send/receive IPv4 multicast for its IPMP group
Answer: DE
Explanation:
FLAGS
Indicates the status of each underlying interface, which can be one or any combination of the following:
(D) d indicates that the interface is down and therefore unusable.
(E) M indicates that the interface is designated by the system to send and receive IPv6 multicast traffic for the IPMP group.
Note:
i indicates that the INACTIVE flag is set for the interface. Therefore, the interface is not used to send or receive data traffic.
s indicates that the interface is configured to be a standby interface.
m indicates that the interface is designated by the system to send and receive IPv4 multicast traffic for the IPMP group.
b indicates that the interface is designated by the system to receive broadcast traffic for the IPMP group.
h indicates that the interface shares a duplicate physical hardware address with another interface and has been taken offline. The h flag indicates that the interface is unusable.
NEW QUESTION 12
Your server has one zone named dbzone (hat has been configured, but not yet installed). Which command would you use to view all the options that were used to configure this zone?
- A. zoneadm list –icv dbzone
- B. zones tat –c summary dbzone
- C. zonecfg –z dbzone info
- D. zonecfg –icv dbzone info
Answer: C
Explanation:
zonecfg info
Display information about the current configuration. If resource-type is specified, displays only information about resources of the relevant type. If any property-name value pairs are specified, displays only information about resources meeting the given criteria. In the resource scope, any arguments are ignored, and info displays information about the resource which is currently being added or modified.
Note: zonecfg –z
zonename. Specify the name of a zone. Zone names are case sensitive. Zone names must begin with an alphanumeric character and can contain alphanumeric characters, the underscore (_) the hyphen (-), and the dot (.). The name global and all names beginning with SUNW are reserved and cannot be used.
Incorrect Answer
A: The zoneadm utility is used to administer system zones. A zone is an application container that is maintained by the operating system runtime.
list option:
Display the name of the current zones, or the specified zone if indicated. B: No such command.
D: no such options zonecfg –icv
NEW QUESTION 13
User jack on host solaris attempts to use ssh to log in to host oracle and receives this message:
jack@solaris:~$ ssh oracle
ssh: connect to host oracle port 22: connection refused What is the problem?
- A. Host oracle does not have a valid host public key.
- B. Host oracle does not have a valid host private key.
- C. Host solaris does not have a valid host public key.
- D. Host does not have a valid host private key.
- E. Host solaris is not configured for host-based authentication.
- F. Host oracle is not configured for host-based authentication.
- G. Host oracle is not running the ssh service.
- H. Host solaris is not running the ssh service.
Answer: G
Explanation:
The host he is trying to connect to (oracle) is not running the required service (ssh).
NEW QUESTION 14
You are installing the Solaris 11 Operation System by using the Text Installer. A panel
prompts you to create a root password and a user account.
Which four describe your options for completing this panel of the Installation?
- A. Creating a user account is optional.
- B. The root password must be set and cannot be blank.
- C. The root password can be left blank.
- D. If you provide a username, that user is assigned the root role.
- E. If you provide a username, that user is given root privileges.
- F. If you provide a username, root is an account rather than a role and is set to expire immediately.
- G. If you do not provide a username, root is an account rather than a role and is set to expire immediately.
Answer: ABDG
Explanation:
A: You are not required to create a user account. B: You must create a root password.
D: If you create a user account in this panel, you need to provide both the user's password and a root password.
In this case, root will be a role assigned to the user.
G: If you do not create a user account, you still need to provide a root password. In this case, root will be a regular user.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two statements are true concerning the network stack on Oracle Solaris 11?
- A. Hardware network interfaces and datalinks have a one-to-one relationship.
- B. IP addresses are assigned to datalinks.
- C. A single IP interface can have either an IPv4 address or an IPv6 address but not both.
- D. A single IP interface can have both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address.
- E. A single datalink can have only one IP interface.
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 16
You have a ZFS file system named /dbase/oral and you want to guarantee that 10 GB of storage space is available to that dataset for all data, snapshots, and clones.
Which option would you choose?
- A. zfs set refreservation=10g dbase/oral
- B. zfs set quota=10g dbase/oral
- C. zfs set refquota=10g dbase/oral
- D. zfs set reservation=10g dbase/oral
Answer: D
Explanation:
A ZFS reservation is an allocation of disk space from the pool that is guaranteed to be available to a dataset. As such, you cannot reserve disk space for a dataset if that space is not currently available in the pool. The total amount of all outstanding, unconsumed reservations cannot exceed the amount of unused disk space in the pool. ZFS reservations can be set and displayed by using the zfs set and zfs get commands. For example:
# zfs set reservation=5G tank/home/bill
# zfs get reservation tank/home/bill NAME PROPERTY VALUE SOURCE
tank/home/bill reservation 5G local
NEW QUESTION 17
Identify the correctly matching pair of equivalent functionality of JumpStart and Automated installer (AI).
- A. JumpStart: begin script AI: package repository
- B. JumpStart: setup_serverAI: installadm create-service
- C. JumpStart: add_Install_clientAI: SMF system configuration profile files
- D. JumpStart: finish scripts and sysidsfg filesAI: manifest files
Answer: B
Explanation:
JumpStart: Use the setup_install_server(1M) command. AI: Use the installadm create-service command.
NEW QUESTION 18
Which two accurately describe the Solaris IPS repository?
- A. It contains a collection of operating system patches.
- B. It contains a collection of software packages.
- C. All packages within an IPS package repository reside in a catalog.
- D. It is an ISO image of the Solaris installation media.
- E. The packages in a catalog are associated with a specific publisher.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
Image Packaging System (IPS) is a new network based package management system included in Oracle Solaris 11. It provides a framework for complete software lifecycle management such as installation, upgrade and removal of software packages. IPS also enables you to create your own software packages, create and manage package repositories, and mirror existing package repositories.
Oracle Solaris software is distributed in IPS packages. IPS packages are stored in IPS package repositories, which are populated by IPS publishers.
E: The following command displays property information about the local repository.
$ pkgrepo get -s /export/repoSolaris11
SECTION PROPERTY VALUE publisher prefix solaris repository description This\ repository\ serves\ a\ copy\ of\ the\ Oracle\ Solaris\ 11\ Build\ 175b\ Package\ Repository. repository name Oracle\ Solaris\ 11\ Build\ 175b\ Package\ Repository
repository version 4
The value of the publisher prefix specifies that solaris is to be used in the following cases:
When more than one publisher's packages are present and no publisher is specified in the package name in the pkg command
When packages are published to the repository and no publisher is specified.
NEW QUESTION 19
Which two SMF milestones can be specified at boot time?
- A. none
- B. network
- C. all
- D. config
- E. unconfig
- F. devices
Answer: AC
Explanation:
The milestones that can be specified at boot time are none
single-user multi-user
multi-user-server all
NEW QUESTION 20
View the Exhibit.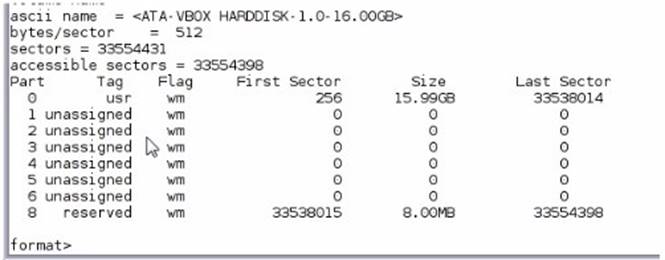
Which is true regarding the disk drive?
- A. This disk configuration could be used as a ZFS root disk.
- B. This disk contains an SMI disk label.
- C. Slice 7 represents the entire disk and cannot be used as a slice for a file system
- D. The disk contains an EFI disk label.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Installing a ZFS Root Pool
The installer searches for a disk based on a recommended size of approximately 13 GB.
NEW QUESTION 21
You are configuring NFS on a server. Select the two statements that are true.
- A. Resources listed in /etc/dfs/dfstab are automatically shared on boot up.
- B. A directory cannot be shared if a subdirectory below it is already shared.
- C. Renaming a share created with the zfs set share command is not supported.
- D. NFS and SMB protocols cannot be used simultaneously to share the same directory.
Answer: AC
Explanation:
A: ZFS can automatically share file systems by setting the sharenfs property. Using this property, you do not have to modify the /etc/dfs/dfstab file when a new file system is shared. The sharenfs property is a comma-separated list of options to pass to the share command. The value on is an alias for the default share options, which provides read/write permissions to anyone. The value off indicates that the file system is not managed by ZFS and can be shared through traditional means, such as the /etc/dfs/dfstab file. All file systems whose sharenfs property is not off are shared during boot.
NEW QUESTION 22
Select two statements that correctly describe the capabilities of the Distribution Constructor.
- A. ISO images for use with the Automated Installer (AI) can be created.
- B. Bootable USB images can be created for SPARC and x86 architectures.
- C. A single installation server can be used to create ISO images for SPARC and x86 architectures.
- D. Checkpoints can be used to pause the build, allowing scripts to run that modify theresulting ISO Image.
- E. A single Installation server can be used to create ISO images for Solaris 10 and Solaris11 operating systems.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
A: You can use the distribution constructor to create the following types of Oracle Solaris images:
* (A) x86 or SPARC ISO Image for Automated Installations
* Oracle Solaris x86 live CD image
* x86 or SPARC Oracle Solaris text installer image
* x86 Oracle Solaris Virtual Machine
Note: You can use the distribution constructor to build custom Oracle Solaris images. Then, you can use the images to install the Oracle Solaris software on individual systems or multiple systems. You can, also, use the distribution constructor to create Virtual Machine (VM) images that run the Oracle Solaris operating system.
D: Checkpointing Options
You can use the options provided in the distro_const command to stop and restart the build process at various stages in the image-generation process, in order to check and debug the image that is being built. This process of stopping and restarting during the build process is called checkpointing.
NEW QUESTION 23
You are going to use the- Automated installer (AI) to install a non global zone named zone1. You have created a custom manifest for the non-global zone and named it zone1manifest
Which command will you use to add this custom manifest to the s11-sparc install service and associate this custom manifest with the non-global zone?
- A. installadm create-profile -n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml - c
- B. installadm create-manifest -n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml -m
- C. installadm create-client -n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml -m zone1manifest -c zonename= “zone1”
- D. installadm create-service - n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml -m zone1manifest - c zonename=”zone1”
Answer: B
Explanation:
installadm add-manifest
Associates manifests with a specific install service, thus making the manifests available on the network, independently from creating a service. When publishing a non-default manifest, it is required to associate criteria either via criteria entered on the command line (-c) or via a criteria XML file (-C).
NEW QUESTION 24
......
Recommend!! Get the Full 1Z0-821 dumps in VCE and PDF From Dumpscollection.com, Welcome to Download: https://www.dumpscollection.net/dumps/1Z0-821/ (New 243 Q&As Version)