It is impossible to pass Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 exam without any help in the short term. Come to Certleader soon and find the most advanced, correct and guaranteed Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 practice questions. You will get a surprising result by our Most recent AWS Certified DevOps Engineer- Professional practice guides.
Online Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 free dumps demo Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
When creating an Elastic Beanstalk environment using the Wizard, what are the 3 configuration options presented to you
- A. Choosingthetypeof Environment- Web or Worker environment
- B. Choosingtheplatformtype-Nodejs,IIS,etc
- C. Choosing the type of Notification - SNS or SQS
- D. Choosing whether you want a highly available environment or not
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
The below screens are what are presented to you when creating an Elastic Beanstalk environment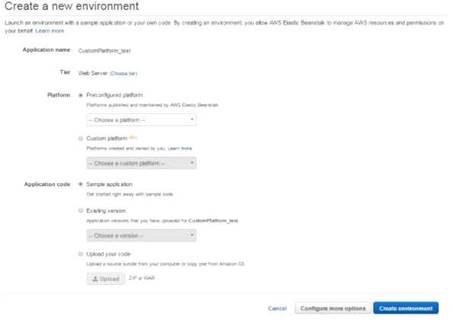
The high availability preset includes a load balancer; the low cost preset does not For more information on the configuration settings, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/environments-create-wizard.html
NEW QUESTION 2
You need to create an audit log of all changes to customer banking data. You use DynamoDB to store this customer banking data. It's important not to lose any information due to server failures. What is an elegant way to accomplish this?
- A. Use a DynamoDB StreamSpecification and stream all changes to AWS Lambd
- B. Log the changes to AWS CloudWatch Logs, removing sensitive information before logging.
- C. Before writing to DynamoDB, do a pre-write acknoledgment to disk on the application server, removing sensitive information before loggin
- D. Periodically rotate these log files into S3.
- E. Use a DynamoDB StreamSpecification and periodically flush to an EC2 instance store, removing sensitive information before putting the object
- F. Periodically flush these batches to S3.
- G. Before writing to DynamoDB, do a pre-write acknoledgment to disk on the application server, removing sensitive information before loggin
- H. Periodically pipe these files into CloudWatch Logs.
Answer: A
Explanation:
You can use Lambda functions as triggers for your Amazon DynamoDB table. Triggers are custom actions you take in response to updates made to the DynamoDB table. To create a trigger, first you enable Amazon DynamoDB Streams for your table. Then, you write a Lambda function to process the updates published to the stream.
For more information on DynamoDB with Lambda, please visit the below URL: http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/with-ddb.html
NEW QUESTION 3
You have an AWS OpsWorks Stack running Chef Version 11.10. Your company hosts its own proprietary cookbook on Amazon S3, and this is specified as a custom cookbook in the stack. You want to use an open-source cookbook located in an external Git repository. What tasks should you perform to enable the use of both custom cookbooks?
- A. Inthe AWS OpsWorks stack settings, enable Berkshel
- B. Create a new cookbook with aBerksfile that specifies the other two cookbook
- C. Configure the stack to usethis new cookbook.
- D. Inthe OpsWorks stack settings add the open source project's cookbook details inaddition to your cookbook.
- E. Contactthe open source project's maintainers and request that they pull your cookbookinto their
- F. Update the stack to use their cookbook.
- G. Inyour cookbook create an S3 symlink object that points to the open sourceproject's cookbook.
Answer: A
Explanation:
To use an external cookbook on an instance, you need a way to install it and manage any dependencies. The preferred approach is to implement a cookbook that supports a dependency manager named Berkshelf. Berkshelf works on Amazon CC2 instances, including AWS OpsWorks Stacks instances, but it is also designed to work with Test Kitchen and Vagrant.
For more information on Opswork and Berkshelf, please visit the link:
• http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/opsworks/latest/userguide/cookbooks-101 -opsworks- berkshelf.htm I
NEW QUESTION 4
You have a set of EC2 Instances in an Autoscaling Group that processes messages from an SQS queue. The messages contain the location in S3 from where video's need to be processed by the EC2 Instances. When a scale in happens, it is noticed that an at times that the EC2 Instance is still in a state of processing a video when the instance is terminated. How can you implement a solution which will ensure this does not happen?
- A. ChangetheCoolDown property for the Auto scaling Group.
- B. SuspendtheAZRebalance termination policy
- C. Use lifecycle hooks to ensure the processing is complete before the termination occurs
- D. Increase the minimum and maximum size for the Auto Scaling group, and change the scaling policies so they scale less dynamically
Answer: C
Explanation:
This is a case where lifecycle policies can be used. The lifecycle policy can be used to put the instance in a state of Terminating:Wait, complete the processing and then send a signal to complete the termination
Auto Scaling lifecycle hooks enable you to perform custom actions by pausing instances as Auto Scaling launches or terminates them. For example, while your newly launched instance is paused, you could install or configure software on it.
For more information on Autoscaling lifecycle hooks, please visit the below U RL:
• http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/lifecycle-hooks.htmI
NEW QUESTION 5
Your CTO thinks your AWS account was hacked. What is the only way to know for certain if there was unauthorized access and what they did, assuming your hackers are very sophisticated AWS engineers and doing everything they can to cover their tracks?
- A. Use CloudTrail Log File Integrity Validation.
- B. Use AWS Config SNS Subscriptions and process events in real time.
- C. Use CloudTrail backed up to AWS S3 and Glacier.
- D. Use AWS Config Timeline forensics.
Answer: A
Explanation:
To determine whether a log file was modified, deleted, or unchanged after CloudTrail delivered it, you can use CloudTrail log file integrity validation. This feature is built using industry standard algorithms: SHA-256 for hashing and SHA-256 with RSA for digital signing. This makes it computationally infeasible to modify, delete or forge CloudTrail log files without detection. You can use the AWS CLI to validate the files in the location where CloudTrail delivered them
Validated log files are invaluable in security and forensic investigations. For example, a validated log file enables you to assert positively that the log file itself has not changed, or that particular user credentials performed specific API activity. The CloudTrail log file integrity validation process also lets you know if a log file has been deleted or changed, or assert positively that no log files were delivered to your account during a given period of time.
For more information on Cloudtrail log file validation, please visit the below URL:
http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/awscloudtrail/latest/userguide/cloudtrai l-log-file-validation- intro.html
NEW QUESTION 6
Which of the following Cloudformation helper scripts can help install packages on EC2 resources
- A. cfn-init
- B. cfn-signal
- C. cfn-get-metadata
- D. cfn-hup
Answer: A
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions
Currently, AWS CloudFormation provides the following helpers:
cf n-init: Used to retrieve and interpret the resource metadata, installing packages, creating files and starting services.
cf n-signal: A simple wrapper to signal an AWS CloudFormation CreationPolicy or WaitCondition,
enabling you to synchronize other resources in the stack with the application being ready.
cf n-get-metadata: A wrapper script making it easy to retrieve either all metadata defined for a resource or path to a specific key or subtree of the resource metadata.
cf n-hup: A daemon to check for updates to metadata and execute custom hooks when the changes are detected. For more information on helper scripts, please visit the below URL: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/cfn-helper-scripts-reference.htmI
NEW QUESTION 7
You are working as an AWS Devops admins for your company. You are in-charge of building the infrastructure for the company's development teams using Cloudformation. The template will include building the VPC and networking components, installing a LAMP stack and securing the created resources. As per the AWS best practices what is the best way to design this template
- A. Create a single cloudformation template to create all the resources since it would be easierfrom the maintenance perspective.
- B. Create multiple cloudformation templates based on the number of VPC's in the environment.
- C. Create multiple cloudformation templates based on the number of development groups in the environment.
- D. Create multiple cloudformation templates for each set of logical resources, one for networking, the otherfor LAMP stack creation.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Creating multiple cloudformation templates is an example of using nested stacks. The advantage of using nested stacks is given below as per the AWS documentation
As your infrastructure grows, common patterns can emerge in which you declare the same components in each of your templates. You can separate out these common components and create dedicated templates for them. That way, you can mix and match different templates but use nested stacks to create a single,
unified stack. Nested stacks are stacks that create other stacks. To create nested stacks, use the AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource in your template to reference
other templates.
For more information on Cloudformation best practices, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
NEW QUESTION 8
Which of the following is the default deployment mechanism used by Elastic Beanstalk when the application is created via Console or EBCLI?
- A. All at Once
- B. Rolling Deployments
- C. Rolling with additional batch
- D. Immutable
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS documentation mentions
AWS Elastic Beanstalk provides several options for how deployments are processed, including deployment policies (All at once. Rolling, Rolling with additional batch,
and Immutable) and options that let you configure batch size and health check behavior during deployments. By default, your environment uses rolling deployments
if you created it with the console or EB CLI, or all at once deployments if you created it with a different client (API, SDK or AWS CLI).
For more information on Elastic Beanstalk deployments, please refer to the below link:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/using-features.rolling-version- deploy.html
NEW QUESTION 9
Your company has developed a web application and is hosting it in an Amazon S3 bucket configured for static website hosting. The application is using the AWS SDK for JavaScript in the browser to access data stored in an Amazon DynamoDB table. How can you ensure that API keys for access to your data in DynamoDB are kept secure?
- A. Create an Amazon S3 role in 1AM with access to the specific DynamoDB tables, and assign it to the bucket hosting your website.
- B. Configure S3 bucket tags with your AWS access keys for your bucket hosing your website so that the application can query them for access.
- C. Configure a web identity federation role within 1AM to enable access to the correct DynamoDB resources and retrieve temporary credentials.
- D. Store AWS keys in global variables within your application and configure the application to use these credentials when making requests.
Answer: C
Explanation:
With web identity federation, you don't need to create custom sign-in code or manage your own user identities. Instead, users of your app can sign in using a well-known identity provider (IdP) — such as Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any other OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compatible IdP, receive an authentication token, and then exchange that token for temporary security credentials in AWS that map to an 1AM role with permissions to use the resources in your AWS account. Using an IdP helps you keep your AWS account secure, because you don't have to embed and distribute long- term security credentials with your application. For more information on Web Identity Federation, please refer to the below document link: from AWS http://docs.wsamazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_providers_oidc.html
NEW QUESTION 10
You are a Devops Engineer for your company. You have been instructed to create a continuous integrated and continuous delivery model for the application in your organization. Which of the below services could be used for this purpose. Choose 2 answers from the options given below
- A. AWSCodeDeploy
- B. AWSCodePipeline
- C. AWSSQS
- D. AWSIAM
Answer: AB
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the below
AWS CodeDeploy is a deployment sen/ice that automates application deployments to Amazon EC2 instances or on-premises instances in your own facility.
You can deploy a nearly unlimited variety of application content, such as code, web and configuration files, executables, packages, scripts, multimedia files, and so on. AWS CodeDeploy can deploy application content stored in Amazon S3 buckets, GitHub repositories, or Bitbucket repositories.
For more information on AWS Code Deploy, please visit the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy/latest/userguide/welcome.html
AWS CodePipeline is a continuous delivery service you can use to model, visualize, and automate the
steps required to release your software. You can quickly model and configure the different stages of a software release process. AWS CodePipeline automates the steps required to release your software changes continuously. For more information on AWS Code Pipeline, please visit the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/latest/userguide/welcome.html
NEW QUESTION 11
Which of the following is not a rolling type update which is present for Configuration Updates when it comes to the Elastic Beanstalk service
- A. Rolling based on Health
- B. Rolling based on Instances
- C. Immutable
- D. Rolling based on time
Answer: B
Explanation:
When you go to the configuration of your Elastic Beanstalk environment, below are the updates that are possible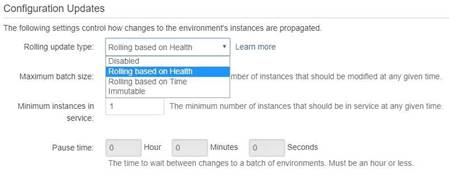
The AWS Documentation mentions
1) With health-based rolling updates. Elastic Beanstalk waits until instances in a batch pass health checks before moving on to the next batch.
2) For time-based rolling updates, you can configure the amount of time that Elastic Beanstalk waits after completing the launch of a batch of instances before moving on to the next batch. This pause time allows your application to bootsrap and start serving requests.
3) Immutable environment updates are an alternative to rolling updates that ensure that configuration changes that require replacing instances are applied efficiently and safely. If an immutable environment update fails, the rollback process requires only terminating an Auto Scalinggroup. A failed rolling update, on the other hand, requires performing an additional rolling update to roll back the changes.
For more information on Rolling updates for Elastic beanstalk configuration updates, please visit the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/using-features.ro11ingupdates.html
NEW QUESTION 12
The AWS Code Deploy service can be used to deploy code from which of the below mentioned source repositories. Choose 3 answers from the options given below
- A. S3Buckets
- B. GitHubrepositories
- C. Subversionrepositories
- D. Bit bucket repositories
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
The AWS documentation mentions the following
You can deploy a nearly unlimited variety of application content, such as code, web and configuration files, executables, packages, scripts, multimedia files, and so on. AWS CodeDeploy can deploy application content stored in Amazon S3 buckets, GitHub repositories, or Bitbucket repositories. You do not need to make changes to your existing code before you can use AWS CodeDeploy.
For more information on AWS Code Deploy, please refer to the below link:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy/latest/userguide/welcome.html
NEW QUESTION 13
You are using Elastic Beanstalk to manage your e-commerce store. The store is based on an open source e- commerce platform and is deployed across multiple instances in an Auto Scaling group. Your development team often creates new "extensions" for the e-commerce store. These extensions include PHP source code as well as an SQL upgrade script used to make any necessary updates to the database schema. You have noticed that some extension deployments fail due to an error when running the SQL upgrade script. After further investigation, you realize that this is because the SQL script is being executed on all of your Amazon EC2 instances. How would you ensure that the SQL script is only executed once per deployment regardless of how many Amazon EC2 instances are running at the time?
- A. Use a "Container command" within an Elastic Beanstalk configuration file to execute the script, ensuring that the "leader only" flag is set to true.
- B. Make use of the Amazon EC2 metadata service to query whether the instance is marked as the leader" in the Auto Scaling grou
- C. Only execute the script if "true" is returned.
- D. Use a "Solo Command" within an Elastic Beanstalk configuration file to execute the scrip
- E. The Elastic Beanstalk service will ensure that the command is only executed once.
- F. Update the Amazon RDS security group to only allow write access from a single instance in the Auto Scaling group; that way, only one instance will successfully execute the script on the database.
Answer: A
Explanation:
You can use the container_commands key to execute commands that affect your application source code. Container commands run after the application and web server have been set up and the application version archive has been extracted, but before the application version is deployed. Non-container commands and other customization operations are performed prior to the application source code being extracted.
You can use leader_only to only run the command on a single instance, or configure a test to only run the command when a test command evaluates to true. Leader-only container commands are only executed during environment creation and deployments, while other commands and server customization operations are performed every time an instance is provisioned or updated. Leader- only container commands are not executed due to launch configuration changes, such as a change in the AMI Id or instance type. For more information on customizing containers, please visit the below URL:
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/customize-containers-ec2.html
NEW QUESTION 14
You are the IT administrator for your company. You have the responsibility of creating development environments which would confirm to the LAMP development stack. The requirement is that the
development team always gets the latest version of the LAMP stack each time a new instance is launched. Which of the following is an efficient and effective way to implement this requirement? Choose 2 answers from the options given below
- A. Create an AMI with all the artifacts of the LAMP stack and provide an instance to the development team based on the AMI.
- B. Create a cloudformation template and use the cloud-init directives to download and the install the LAMP stack packages.
- C. Use the User data section and use a custom script which will be used to download the necessary LAMP stack packages.
- D. Create an EBS Volume with the LAMP stack and attach it to an instance whenever it is required.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
Using User data and cloud-init directives you can always ensure you download the latest version of the LAMP stack and give it to the development teams. With AMI's
you will always have the same version and will need to create an AMI everytime the version of the LAMP stack changes.
The AWS Documentation mentions
When you launch an instance in Amazon CC2, you have the option of passing user data to the instance that can be used to perform common automated configuration tasks and even run scripts after the instance starts. You can pass two types of user data to Amazon CC2: shell scripts and cloud-init directives. You can
also pass this data into the launch wizard as plain text, as a file (this is useful for launching instances using the command line tools), or as base64-encoded text (for API calls).
For more information on User data please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCC2/latest/UserGuide/user-data.html
NEW QUESTION 15
Your security officer has told you that you need to tighten up the logging of all events that occur on your AWS account. He wants to be able to access all events that occur on the account across all regions quickly and in the simplest way possible. He also wants to make sure he is the only person that has access to these events in the most secure way possible. Which of the following would be the best solution to assure his requirements are met? Choose the correct answer from the options below
- A. Use CloudTrail to logall events to one S3 bucke
- B. Make this S3 bucket only accessible by your security officer with a bucket policy that restricts access to his user only and also add MFA to the policy for a further level of securit
- C. ^/
- D. Use CloudTrail to log all events to an Amazon Glacier Vaul
- E. Make sure the vault access policy only grants access to the security officer's IP address.
- F. Use CloudTrail to send all API calls to CloudWatch and send an email to the security officer every time an API call is mad
- G. Make sure the emails are encrypted.
- H. Use CloudTrail to log all events to a separate S3 bucket in each region as CloudTrail cannot write to a bucket in a different regio
- I. Use MFA and bucket policies on all the different buckets.
Answer: A
Explanation:
AWS CloudTrail is a service that enables governance, compliance, operational auditing, and risk auditing of your AWS account. With CloudTrail, you can log,
continuously monitor, and retain events related to API calls across your AWS infrastructure. CloudTrail provides a history of AWS API calls for your account, including API calls made through the AWS Management Console, AWS SDKs, command line tools, and other AWS services. This history simplifies security analysis, resource change tracking, and troubleshooting.
You can design cloudtrail to send all logs to a central S3 bucket. For more information on cloudtrail, please visit the below URL:
◆ https://aws.amazon.com/cloudtrail/
NEW QUESTION 16
Which of the following are ways to ensure that data is secured while in transit when using the AWS Elastic load balancer. Choose 2 answers from the options given below
- A. Usea TCP front end listener for your ELB
- B. Usean SSL front end listenerforyourELB
- C. Usean HTTP front end listener for your ELB
- D. Usean HTTPS front end listener for your ELB
Answer: BD
Explanation:
The AWS documentation mentions the following
You can create a load balancer that uses the SSL/TLS protocol for encrypted connections (also known as SSL offload). This feature enables traffic encryption between your load balancer and the clients that initiate HTTPS sessions, and for connections between your load balancer and your L~C2 instances.
For more information on Elastic Load balancer and secure listeners, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/elb-https-load-balancers.html
NEW QUESTION 17
When deploying applications to Elastic Beanstalk, which of the following statements is false with regards to application deployment
- A. Theapplication can be bundled in a zip file
- B. Caninclude parent directories
- C. Shouldnot exceed 512 MB in size
- D. Canbe a war file which can be deployed to the application server
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions
When you use the AWS Clastic Beanstalk console to deploy a new application or an application version, you'll need to upload a source bundle. Your source bundle must meet the following requirements:
Consist of a single ZIP file or WAR file (you can include multiple WAR files inside your ZIP file) Not exceed 512 MB
Not include a parent folder or top-level directory (subdirectories are fine)
For more information on deploying applications to Clastic Beanstalk please see the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/applications-sourcebundle.html
NEW QUESTION 18
When you add lifecycle hooks to an Autoscaling Group, what are the wait states that occur during the scale in and scale out process. Choose 2 answers from the options given below
- A. Launching:Wait
- B. Exiting:Wait
- C. Pending:Wait
- D. Terminating:Wait
Answer: CD
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
After you add lifecycle hooks to your Auto Scaling group, they work as follows:
1. Auto Scaling responds to scale out events by launching instances and scale in events by terminating instances.
2. Auto Scaling puts the instance into a wait state (Pending:Wait orTerminating: Wait). The instance is paused until either you tell Auto Scaling to continue or the timeout period ends.
For more information on Autoscaling Lifecycle hooks, please visit the below URL: • http://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/lifecycle-hooks.htmI
NEW QUESTION 19
Your serverless architecture using AWS API Gateway, AWS Lambda, and AWS DynamoDB experienced a large increase in traffic to a sustained 3000 requests per second, and dramatically increased in failure rates. Your requests, during normal operation, last 500 milliseconds on average. Your DynamoDB table did not exceed 50% of provisioned throughput, and Table primary keys are designed correctly. What is the most likely issue?
- A. Your API Gateway deployment is throttling your requests.
- B. Your AWS API Gateway Deployment is bottleneckingon request (deserialization.
- C. You did not request a limit increase on concurrent Lambda function executions.
- D. You used Consistent Read requests on DynamoDB and are experiencing semaphore lock.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Every Lambda function is allocated with a fixed amount of specific resources regardless of the memory allocation, and each function is allocated with a fixed amount of code storage per function and per account.
By default, AWS Lambda limits the total concurrent executions across all functions within a given region to 1000.
For more information on Concurrent executions, please visit the below URL: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/concurrent-executions.htmI
NEW QUESTION 20
You have an application hosted in AWS, which sits on EC2 Instances behind an Elastic Load Balancer. You have added a new feature to your application and are now receving complaints from users that the site has a slow response. Which of the below actions can you carry out to help you pinpoint the issue
- A. Use Cloudtrail to log all the API calls, and then traverse the log files to locate the issue
- B. Use Cloudwatch, monitor the CPU utilization to see the times when the CPU peaked
- C. Reviewthe Elastic Load Balancer logs
- D. Create some custom Cloudwatch metrics which are pertinent to the key features of your application
Answer: D
Explanation:
Since the issue is occuring after the new feature has been added, it could be relevant to the new feature.
Enabling Cloudtrail will just monitor all the API calls of all services and will not benefit the cause.
The monitoring of CPU utilization will just reverify that there is an issue but will not help pinpoint the issue.
The Elastic Load Balancer logs will also just reverify that there is an issue but will not help pinpoint the issue.
For more information on custom Cloudwatch metrics, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/publishingMetrics.html
NEW QUESTION 21
You are using Elastic Beanstalk for your development team. You are responsible for deploying multiple versions of your application. How can you ensure, in an ideal way, that you don't cross the application version limit in Elastic beanstalk?
- A. Createa lambda function to delete the older versions.
- B. Createa script to delete the older versions.
- C. UseAWSConfig to delete the older versions
- D. Uselifecyle policies in Elastic beanstalk
Answer: D
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions
Each time you upload a new version of your application with the Clastic Beanstalk console or the CB CLI, Elastic Beanstalk creates an application version. If you don't delete versions that you no longer use, you will eventually reach the application version limit and be unable to create new versions of that application.
You can avoid hitting the limit by applying an application version lifecycle policy to your applications.
A lifecycle policy tells Clastic Beanstalk to delete application versions that are old, or to delete application versions when the total number of versions for an application exceeds a specified number.
For more information on Clastic Beanstalk lifecycle policies please see the below link:
• http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/appl ications-lifecycle.html
NEW QUESTION 22
The company you work for has a huge amount of infrastructure built on AWS. However there has been some concerns recently about the security of this infrastructure, and an external auditor has been given the task of running a thorough check of all of your company's AWS assets. The auditor will be in the USA while your company's infrastructure resides in the Asia Pacific (Sydney) region on AWS. Initially, he needs to check all of your VPC assets, specifically, security groups and NACLs You have been assigned the task of providing the auditor with a login to be able to do this. Which of the following would be the best and most secure solution to provide the auditor with so he can begin his initial investigations? Choose the correct answer from the options below
- A. Create an 1AM user tied to an administrator rol
- B. Also provide an additional level of security with MFA.
- C. Give him root access to your AWS Infrastructure, because he is an auditor he will need access to every service.
- D. Create an 1AM user who will have read-only access to your AWS VPC infrastructure and provide the auditor with those credentials.
- E. Create an 1AM user with full VPC access but set a condition that will not allow him to modify anything if the request is from any IP other than his own.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Generally you should refrain from giving high level permissions and give only the required permissions. In this case option C fits well by just providing the relevant access which is required.
For more information on 1AM please see the below link:
• https://aws.amazon.com/iam/
NEW QUESTION 23
......
Recommend!! Get the Full DOP-C01 dumps in VCE and PDF From Dumps-hub.com, Welcome to Download: https://www.dumps-hub.com/DOP-C01-dumps.html (New 116 Q&As Version)